Government project implementation plays a crucial role in shaping public services and infrastructure. It involves careful planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure taxpayer money is used effectively. The Government Project Delivery Function brings together experts who advise on and manage project development across various departments.
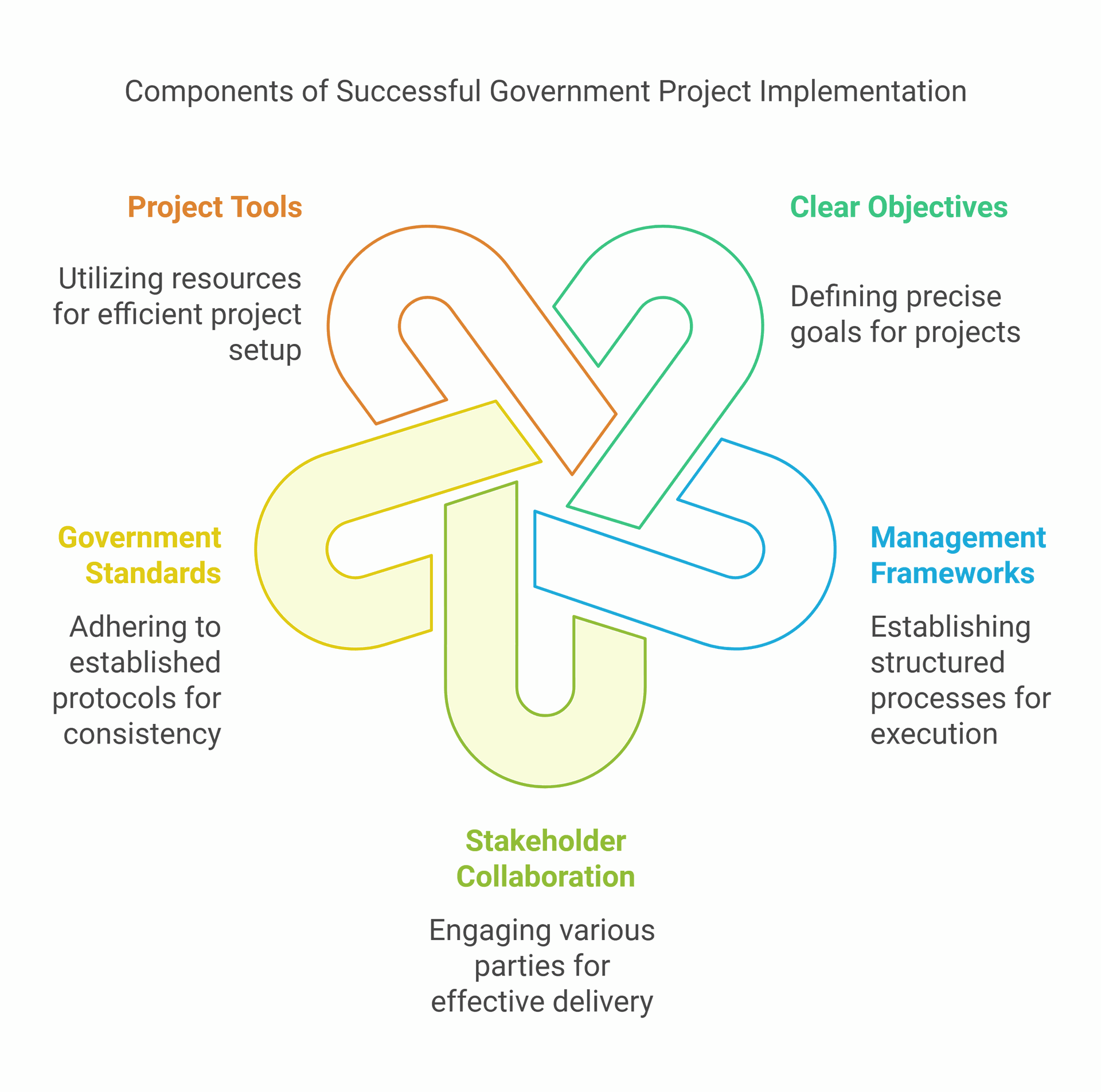
Successful government project implementation relies on clear objectives, robust management frameworks, and effective collaboration between stakeholders. The Government Functional Project Delivery Standard sets out expectations for managing portfolios, programmes, and projects. This standard helps ensure consistency and best practices across different government initiatives.
To improve project outcomes, the government has developed tools like the Project Set Up Toolkit. These resources help teams frame opportunities, define outcomes, and navigate complex projects. By following these guidelines, government agencies can increase the chances of delivering projects on time, within budget, and with the intended benefits for the public.
Key Takeaways
- Government project implementation requires careful planning and expert management to ensure effective use of public resources
- Tools and standards are in place to guide project delivery across different government departments
- Successful projects rely on clear objectives, stakeholder collaboration, and adherence to best practices
Understanding Government Project Implementation
Government project implementation is a complex process that involves careful planning, execution, and monitoring. It aims to turn policies into tangible outcomes that benefit citizens and improve public services.
Fundamentals of Government Projects
Government projects are initiatives undertaken to achieve specific goals aligned with public policy objectives. These projects often involve large budgets, multiple stakeholders, and complex regulations. Key elements include:
• Clear objectives and scope • Defined timelines and milestones
• Allocated resources (human and financial)
• Risk management strategies
• Performance metrics
Successful government projects require strong leadership, effective communication, and robust governance structures. They must also adapt to changing political landscapes and public needs.
The Project Lifecycle in Government
The lifecycle of government projects typically follows these stages:
- Initiation: Identifying needs and developing the business case
- Planning: Defining scope, timelines, and resource requirements
- Execution: Implementing the project plan and delivering outputs
- Monitoring and Control: Tracking progress and managing risks
- Closure: Evaluating outcomes and capturing lessons learned
The Government Functional Project Delivery Standard provides a framework for managing projects across these stages. It emphasises the importance of continuous improvement and stakeholder engagement throughout the process.
Strategic Objectives and Policy Alignment
Government projects must align with broader strategic objectives and policy goals. This alignment ensures that resources are used effectively to address national priorities. Key considerations include:
• Contribution to government priorities
• Consistency with departmental strategies
• Support for policy implementation
• Measurable impact on public services
The Project Outcome Profile tool helps teams link project outputs to strategic outcomes. It encourages a focus on long-term benefits rather than short-term deliverables.
Effective alignment requires collaboration across government departments and levels. It also demands a clear understanding of how project outcomes contribute to wider policy objectives.
Planning and Design
Good planning and design are key to successful government project implementation. These steps lay the groundwork for smooth execution and help prevent costly mistakes.
Developing Effective Business Cases
A solid business case is vital for any government project. It outlines the project's goals, benefits, and costs. Here are key elements:
• Clear objectives aligned with government priorities
• Detailed cost-benefit analysis
• Timeline and milestones
• Resource requirements
Business cases should be evidence-based and thorough. They must show how the project will deliver value for taxpayers' money.
Strong business cases help secure funding and support from decision-makers. They also serve as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle.
Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management is crucial for government projects. It involves identifying, assessing, and planning for potential issues. Common strategies include:
- Risk identification workshops
- Probability and impact assessments
- Risk mitigation planning
- Regular risk reviews
Tools and techniques can help teams manage risks systematically. These might include risk registers and heat maps.
Good risk management helps projects stay on track and within budget. It also improves decision-making and stakeholder confidence.
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is critical for government project success. It involves identifying and engaging with all parties affected by or interested in the project. Key steps include:
• Stakeholder mapping
• Communication planning
• Regular updates and feedback sessions
Effective stakeholder management builds trust and support. It helps address concerns early and can prevent opposition later.
Project leaders should prioritise stakeholder engagement throughout the project lifecycle. This ensures all voices are heard and increases the likelihood of project success.
Project Management Frameworks
The UK government employs robust project management frameworks to ensure efficient delivery of initiatives. These frameworks provide structure, standardisation, and continuous improvement mechanisms for project implementation across various departments and agencies.
Adopting Standard Methodologies
The government utilises widely recognised project management methodologies to streamline processes. PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a popular choice, offering a structured approach to project management. This method divides projects into manageable stages, with clear roles and responsibilities.
Another framework gaining traction is Agile, which allows for flexibility and rapid adaptation to changing requirements. Many departments use a hybrid approach, combining elements of PRINCE2 and Agile to suit specific project needs.
The Project Management Institute (PMI) and Association for Project Management (APM) provide additional guidance and certifications for project professionals in the UK public sector.
Role of the Infrastructure and Projects Authority
The Infrastructure and Projects Authority (IPA) plays a crucial role in overseeing major government projects. This organisation sets standards, provides support, and ensures consistency across departments.
The IPA developed the Government Functional Project Delivery Standard, which outlines expectations for managing portfolios, programmes, and projects. This standard helps align project delivery with government priorities and improves outcomes.
The IPA also offers training and development programmes for project professionals, enhancing skills and capabilities across the civil service.
Continuous Improvement and Best Practices
The UK government emphasises ongoing improvement in project management practices. The Continuous Improvement Assessment Framework allows organisations to evaluate their performance against set standards and plan targeted enhancements.
Best practices are shared through various channels, including:
- Regular workshops and seminars
- Case studies of successful projects
- Peer reviews and knowledge sharing sessions
The Major Projects Association facilitates networking and learning opportunities for professionals involved in large-scale government initiatives.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, the government aims to increase project success rates and deliver better value for taxpayers.
Performance and Quality
Effective performance measurement and quality control are vital for successful government project implementation. These elements ensure projects meet objectives, deliver value, and satisfy stakeholders.
Benchmarking and Performance Metrics
Benchmarking helps compare project performance against industry standards. It allows teams to set realistic targets and identify areas for improvement.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial for tracking progress. These may include cost efficiency, schedule adherence, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Data-driven performance is a growing trend in government projects. Analytics tools can process large datasets to provide insights and inform decision-making.
Regular performance reviews help keep projects on track. These should involve all key stakeholders and focus on addressing any issues promptly.
Quality Assurance and Control
Quality assurance (QA) processes ensure projects meet required standards. This involves setting clear quality objectives and implementing checks throughout the project lifecycle.
Quality control (QC) measures verify that deliverables meet specifications. This may include testing, inspections, and peer reviews.
Documentation is essential for maintaining quality. Detailed records of processes, decisions, and changes support accountability and enable continuous improvement.
Training staff in quality management techniques can boost overall project performance. This creates a culture of excellence and reduces the risk of errors.
Achieving Project Success
Clear goals and objectives are fundamental to project success. These should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Effective communication is key. Regular updates keep stakeholders informed and engaged, fostering support for the project.
Risk management is crucial for navigating challenges. Identifying potential issues early allows for proactive mitigation strategies.
Flexibility and adaptability help projects respond to changing circumstances. Agile methodologies can be particularly effective in dynamic environments.
Celebrating milestones and successes boosts team morale. Recognising achievements, both big and small, helps maintain motivation throughout the project.
Innovation in Project Delivery
The UK government is embracing cutting-edge technologies and methods to improve project delivery. These innovations aim to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance outcomes for public initiatives.
Leveraging Data and AI
AI and data analytics are transforming government project delivery. Machine learning algorithms can analyse vast amounts of project data to identify patterns and predict potential issues. This allows teams to take proactive measures and make informed decisions.
AI-powered tools help automate routine tasks, freeing up project managers to focus on strategic work. For example, chatbots can handle simple queries, while AI assists in resource allocation and risk assessment.
Data-driven insights enable more accurate project planning and forecasting. By analysing historical data, teams can better estimate timelines and budgets for similar future projects.
Digital Transformation Initiatives
The government is investing in digital transformation to modernise project delivery methods. Cloud-based project management platforms allow for real-time collaboration and information sharing across teams and departments.
Digital twin technology is being used in infrastructure projects to create virtual models. These allow teams to simulate various scenarios and optimise designs before construction begins.
Agile methodologies are being adopted to increase flexibility and responsiveness in project delivery. This approach enables teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements and deliver value incrementally.
Advancing the Project Delivery Profession
The Government Project Delivery Profession is working to build a skilled workforce equipped to handle modern project challenges. Training programmes focus on developing digital skills and fostering innovation mindsets.
Communities of practice are being established to share knowledge and best practices across departments. These networks help spread innovative approaches and lessons learned.
The profession is also creating new roles and career paths that reflect the changing nature of project delivery. Specialists in data analytics, digital transformation, and AI are now integral to many project teams.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Effective partnerships and collaborative approaches are crucial for successful government project implementation. These strategies enhance service delivery, optimise resource utilisation, and foster innovation across public and private sectors.
Engaging with Delivery Partners
Government projects often rely on partnerships with various organisations to achieve their goals. Delivery partners may include local authorities, charities, and private firms. These partnerships help leverage diverse expertise and resources.
Key steps for engaging delivery partners:
- Identify suitable partners based on project needs
- Establish clear communication channels
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Set shared objectives and performance metrics
Regular meetings and progress reviews ensure alignment between all parties. This approach helps address challenges promptly and keeps projects on track.
Collaborative Approaches to Infrastructure
Infrastructure projects benefit greatly from collaboration between government agencies, local communities, and industry experts. This approach ensures that projects meet public needs while incorporating cutting-edge solutions.
Transforming Infrastructure Performance initiatives focus on:
- Implementing digital technologies for better project management
- Adopting sustainable construction methods
- Enhancing skills and capabilities within the workforce
These collaborative efforts lead to more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly infrastructure developments.
Public and Private Sector Synergies
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are a powerful tool for delivering complex government projects. They combine public sector oversight with private sector innovation and efficiency.
Benefits of PPPs include:
- Shared financial risks
- Access to specialised private sector expertise
- Improved project delivery timelines
Successful PPPs require careful planning and robust governance structures. They often involve long-term contracts that outline performance standards, risk allocation, and payment mechanisms.
By fostering these synergies, governments can deliver high-quality services and infrastructure while maximising value for taxpayers.
Financial and Resource Management
Effective financial and resource management is crucial for successful government project implementation. It involves strategic allocation of funds, careful cost control, and planning for long-term sustainability.
Public Investment and Resource Allocation
Public investment plays a key role in driving economic growth. Governments must carefully allocate limited resources to maximise public benefit. This requires thorough analysis of potential projects and their expected returns.
Project financial management procedures help ensure funds are used properly. These often include:
• Setting up designated project accounts
• Tracking expenditures against budgets
• Regular financial reporting
Transparent processes for resource allocation help build public trust. They also allow for better scrutiny of spending decisions.
Cost Management and Avoiding Scope Creep
Controlling costs is vital for project success. Careful planning and monitoring help prevent budget overruns. Project accounting practices should include:
• Detailed cost forecasting
• Tracking of actual vs. budgeted spending
• Regular financial reviews
Scope creep is a common issue that can inflate costs. Clear project boundaries and change control processes are essential. These help avoid unnecessary additions that drain resources.
Regular stakeholder communication about project scope and budget constraints is crucial. This keeps everyone aligned on project goals and limitations.
Sustainability and Long-term Viability
Projects must be designed with long-term sustainability in mind. This includes planning for ongoing maintenance and operational costs. Failure to do so can lead to abandoned or underused facilities.
Environmental sustainability is increasingly important. Projects should consider their carbon footprint and impact on natural resources. This may involve:
• Using eco-friendly materials
• Incorporating energy-efficient designs
• Planning for waste reduction
Financial sustainability requires careful forecasting of future costs and revenues. Projects should have clear plans for funding ongoing operations. This might include user fees, government subsidies, or other revenue streams.
Challenges in Government Project Implementation
Government projects face unique hurdles that can hinder their success. These challenges stem from complex organisational structures, data management issues, and evolving project requirements.
Tackling Transformation Challenges
Transformation projects in the public sector often struggle due to their scale and complexity. Large-scale changes to systems and processes can be daunting for staff and citizens alike.
E-government initiatives, for example, aim to modernise services but face resistance. Legacy systems and entrenched work practices make transitions difficult. Staff may lack the skills needed to operate new digital platforms.
Effective change management is crucial. Leaders must communicate the vision clearly and provide adequate training. Phased rollouts can help ease the transition and allow for adjustments.
• Create a detailed transformation roadmap
• Engage stakeholders early and often
• Provide comprehensive training programmes
• Monitor progress and adjust plans as needed
Data Sharing and Information Management
Governments handle vast amounts of sensitive data. Sharing this information across departments and agencies is vital for efficient operations. However, privacy concerns and technical barriers often impede data flow.
Incompatible systems between agencies can make data sharing difficult. Security protocols may be overly restrictive, limiting access to necessary information. Privacy laws can also create confusion about what data can be shared and with whom.
To address these issues, governments must:
- Develop clear data sharing policies
- Invest in interoperable IT systems
- Implement robust data protection measures
- Train staff on proper data handling procedures
Adapting to Changing Requirements
Government projects often span years, during which political priorities and public needs can shift dramatically. This flux can lead to scope creep, budget overruns, and delayed deliverables.
Agile project management methodologies can help teams respond to change more effectively. Breaking large projects into smaller, manageable chunks allows for greater flexibility. Regular reviews and adjustments keep projects aligned with current needs.
Key strategies include:
- Setting clear, measurable objectives
- Conducting frequent stakeholder consultations
- Maintaining flexible budgets and timelines
- Employing iterative development approaches
By embracing these practices, government agencies can improve their ability to deliver successful projects despite changing circumstances.
Future Outlook and Innovations
New technologies and changing organisational structures are reshaping government project implementation. These advances aim to improve efficiency, collaboration, and strategic alignment in public sector programmes.
Evolving Technologies in Project Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming project management tools. These technologies help predict risks, optimise resource allocation, and automate routine tasks. Cloud-based platforms enable real-time collaboration across departments and agencies.
Data analytics provides deeper insights into project performance. Predictive models can forecast outcomes and guide decision-making. Virtual and augmented reality allow teams to visualise complex projects before implementation.
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and security in government contracts. It creates tamper-proof records of transactions and milestones. This improves accountability and reduces disputes.
Reshaping Organisational Structures
Government agencies are adopting more flexible and agile structures. Cross-functional teams replace rigid hierarchies, fostering innovation and rapid problem-solving. Matrix organisations allow for better resource sharing across projects.
Project delivery functions are evolving to meet new challenges. Specialised project management offices (PMOs) provide centralised support and oversight. These PMOs help standardise practices and drive continuous improvement.
Collaborative networks are forming between government, industry, and academia. These partnerships bring diverse expertise to complex public sector projects. They also promote knowledge sharing and best practice adoption.
Meeting Tomorrow's Strategic Goals
Future-focused project management aligns with long-term government strategies. The UK Innovation Strategy emphasises projects that drive economic growth and societal benefits.
Sustainability is becoming a key factor in project selection and design. Green technologies and circular economy principles are integrated into infrastructure projects. This supports national environmental targets and improves long-term value.
Skills development is crucial for delivering tomorrow's projects. Training programmes focus on emerging technologies and adaptive management techniques. This ensures the public sector workforce can meet future challenges effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Government project implementation involves key steps, frameworks, plans, guidelines, challenges, and ongoing evolution. These elements shape how public initiatives are executed and their ultimate outcomes.
What are the key steps in the implementation of a government project?
Government projects typically start with planning and approval. This includes defining objectives, securing funding, and outlining timelines.
Next comes resource allocation and team formation. Skilled personnel are assigned roles and responsibilities.
The execution phase follows, where the project plan is put into action. Regular monitoring and reporting ensure progress stays on track.
How does a project management framework affect government project outcomes?
A solid framework provides structure and guidance. It helps teams stay organised and focused on project goals.
Project management frameworks can improve communication and decision-making. They often include tools for risk assessment and quality control.
Frameworks also aid in resource allocation and timeline management. This can lead to more efficient use of public funds and timely project completion.
What is typically included in a government project implementation plan?
A comprehensive plan outlines project scope, objectives, and deliverables. It includes a detailed timeline with milestones and deadlines.
Budget information is crucial, detailing expected costs and funding sources. The plan also lists required resources, including personnel and equipment.
Risk management strategies and contingency plans are often included. These help teams prepare for potential setbacks or changes.
How are government project guidelines developed and enforced?
Guidelines are often created by experienced project managers and policymakers. They draw on past successes and lessons learned from previous projects.
Government agencies may establish standardised procedures and best practices. These are often reviewed and updated regularly to stay current.
Enforcement typically involves oversight committees and regular audits. Project teams may be required to submit progress reports and documentation to ensure compliance.
What are common challenges faced during the government project implementation phase?
Budget constraints and funding issues can hinder progress. Unexpected costs or delays may strain allocated resources.
Bureaucratic red tape can slow decision-making and approvals. This can lead to missed deadlines and increased costs.
Changing political landscapes may affect project priorities. New administrations might alter or cancel ongoing initiatives.
Can you demonstrate how government project implementation has evolved in recent years?
Recent years have seen increased use of digital tools and platforms. These help streamline communication and data management.
There's greater emphasis on transparency and public engagement. Many agencies now involve citizens in the planning and feedback process.
Agile methodologies have gained popularity in government projects. This allows for more flexibility and responsiveness to changing needs.