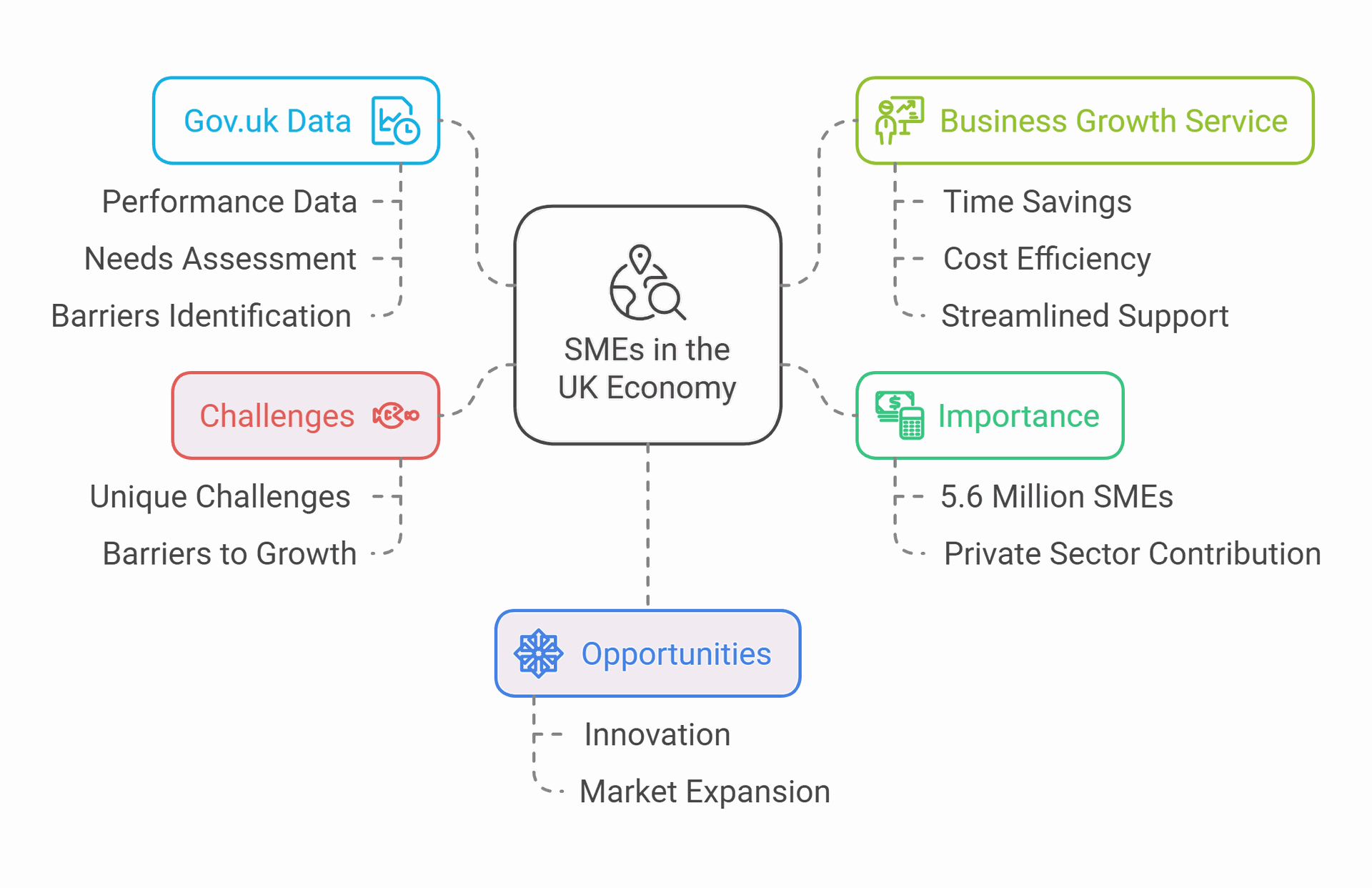
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are vital to the UK economy. The government offers many resources to help these businesses grow. By using data from gov.uk, SMEs can make smart choices about their future.
The UK has nearly 5.6 million SMEs, making up a huge part of the private sector. These firms face unique challenges and opportunities. Gov.uk provides data on SME performance, needs, and barriers to growth. This information can help business owners make better decisions.
Using gov.uk data, SMEs can find advice and support all in one place. The Business Growth Service aims to save firms time and money. It makes it easier to get help from the government. This can lead to faster growth and more success for small businesses across the UK.
Key Takeaways
- Gov.uk offers valuable data and resources for SME growth and development
- The Business Growth Service streamlines government support for small firms
- SMEs play a crucial role in the UK's economic landscape and innovation
Understanding SMEs in the UK Context
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are vital to the UK economy. They make up a large portion of businesses and contribute significantly to employment and economic growth.
SME Statistics and Business Population
SMEs form the backbone of UK businesses. They account for 99% of the business population. This shows their crucial role in the economy.
The total number of UK businesses has changed in recent years. Between 2020 and 2021, it fell by 6.5%. This was only the second decline since 2000.
SMEs come in different sizes:
- Micro-businesses (0-9 employees)
- Small businesses (10-49 employees)
- Medium-sized businesses (50-249 employees)
The UK government uses the European Commission's definition of SMEs for spending purposes.
Economic Impact of SMEs on the UK Economy
SMEs play a key role in job creation and economic growth. They provide employment opportunities across various sectors and regions.
SMEs contribute to:
- Innovation and competition
- Local economic development
- Supply chain diversity
The government recognises their importance. It aims to support SMEs through various initiatives and policies.
Crown Commercial Service's SME Action Plan outlines efforts to level the playing field for SMEs in government contracts.
Variety of SMEs across Sectors
SMEs operate in diverse sectors of the UK economy. They range from traditional industries to cutting-edge technology firms.
Key sectors with strong SME presence include:
- Retail and hospitality
- Professional services
- Manufacturing
- Technology and digital
The government tracks SME performance through surveys. The SME business barometer assesses their performance, needs, and growth barriers.
This data helps policymakers understand SME challenges and opportunities. It informs targeted support measures and policies to foster SME growth across different sectors.
Factors Influencing SME Growth
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face various challenges and opportunities that impact their growth potential. Key factors include innovation capabilities, skill levels, productivity enhancements, and overcoming growth barriers.
The Role of Innovation and Skills
Innovation drives SME growth by creating new products and improving processes. 76% of SMEs aimed to increase sales over three years, highlighting growth ambitions. To achieve this, businesses need skilled workers.
Management skills are crucial for guiding SMEs through growth phases. Leaders must:
- Develop strategic plans
- Manage finances effectively
- Build strong teams
Investing in employee training boosts productivity and innovation. This can involve:
- Technical skills development
- Soft skills enhancement
- Continuous learning programmes
Challenges in Enhancing Productivity
Productivity improvements are vital for SME growth. Yet, many firms struggle to boost efficiency. Common challenges include:
- Limited access to technology
- Inefficient processes
- Lack of data-driven decision making
Rising costs affected growth plans for 55% of SMEs. This highlights the need for cost-effective productivity solutions. SMEs can focus on:
- Streamlining operations
- Adopting digital tools
- Optimising resource allocation
Improving productivity often requires initial investment. SMEs must balance short-term costs with long-term benefits.
Identifying Barriers to Business Growth
SMEs face numerous obstacles that hinder growth. Recognising these barriers is the first step to overcoming them. Common growth barriers include:
- Limited access to finance
- Regulatory burdens
- Market competition
- Skills shortages
The UK government tracks SME performance and growth factors through regular surveys. This data helps identify sector-specific challenges.
To address these barriers, SMEs can:
- Seek government support and advice
- Network with other businesses
- Invest in market research
- Develop tailored growth strategies
By tackling these obstacles, SMEs can unlock their growth potential and contribute to broader economic growth.
Financial Landscape for SME Development
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the UK face unique financial challenges and opportunities. The government offers various forms of support to help these businesses thrive and contribute to economic growth.
Tax Relief and Fiscal Support for SMEs
SMEs can benefit from several tax relief schemes. The Research and Development (R&D) tax credits allow companies to deduct a percentage of their R&D costs from their annual tax bill. This encourages innovation and growth.
The VAT registration threshold stands at £85,000, giving smaller businesses some flexibility in managing their tax obligations. SMEs can also take advantage of the Annual Investment Allowance, which lets them deduct the full value of qualifying plant and machinery up to a set amount.
Employment Allowance reduces employers' National Insurance contributions, making it easier for SMEs to hire and retain staff.
Late Payments and Cash Flow Management
Late payments pose a significant challenge for SMEs, often causing cash flow issues. The government has introduced measures to address this problem:
- The Prompt Payment Code requires signatories to pay 95% of invoices within 60 days
- The Small Business Commissioner helps SMEs resolve payment disputes
- The Late Payment of Commercial Debts Act allows businesses to claim interest on overdue payments
SMEs can improve cash flow by:
- Offering early payment discounts
- Using invoice financing
- Implementing robust credit control procedures
Access to Loans and Financial Support
The UK government provides various avenues for SMEs to access finance. The British Business Bank offers several programmes, including:
- Start Up Loans: Unsecured personal loans up to £25,000 for new businesses
- Enterprise Finance Guarantee: Facilitates lending to viable SMEs lacking adequate security
- Regional funds: Targeted support for businesses in specific areas
Commercial banks also offer specialised SME lending products. The government encourages these institutions to increase their SME lending through initiatives like the Bank Referral Scheme.
Alternative finance options, such as peer-to-peer lending and crowdfunding, have grown in popularity, providing SMEs with more choices for funding their growth.
Legislative Frameworks Affecting SMEs
The UK government has established key regulations to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in their growth and participation in the economy. These frameworks aim to level the playing field and create opportunities for SMEs to compete with larger businesses.
Navigating the Procurement Act for SME Inclusion
The Procurement Act sets out guidelines to increase SME involvement in government contracts. It requires public sector organisations to consider breaking larger contracts into smaller lots, making them more accessible to SMEs.
Key features of the Act include:
• Simplified bidding processes • Reduced administrative burdens • Prompt payment clauses
These measures help SMEs compete more effectively against large businesses for government tenders. The Act also encourages public sector buyers to engage with SMEs early in the procurement process, fostering innovation and diverse supply chains.
Compliance with Employment and SME Regulations
SME employers must adhere to various regulations designed to protect workers and promote fair business practices. These rules apply to private sector businesses of all sizes but often have specific provisions for SMEs.
Important areas of compliance include:
• National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage • Workplace pension auto-enrolment • Health and safety standards • Equal opportunities and anti-discrimination policies
The government provides guidance and support to help SMEs understand and implement these regulations. This ensures that smaller businesses can maintain high standards of employment practices without facing undue burdens.
Exploring SME Leadership and Management
Leadership and management skills are vital for SME success. They drive growth, boost productivity, and help businesses adapt to challenges.
Developing Strong Leadership within SMEs
SME leaders play a key role in setting the direction and culture of their organisations. Strong leadership skills are essential for guiding teams and making strategic decisions.
Effective SME leaders:
- Communicate a clear vision
- Inspire and motivate employees
- Make tough decisions under pressure
- Adapt to changing market conditions
Leadership development programmes can help SME owners enhance their skills. These may include coaching, mentoring, and workshops focused on strategic thinking and team management.
Many SMEs struggle with leadership succession. Planning for future leadership needs is crucial for long-term success and stability.
Building Management Skills and Capacity
Management skills are critical for day-to-day operations and achieving business goals. Improving management capabilities can lead to higher turnover and increased employee satisfaction.
Key management skills for SMEs include:
- Financial planning and budgeting
- Human resource management
- Project management
- Performance monitoring and evaluation
Training and development programmes can help SME managers build these skills. Online courses, workshops, and industry-specific training can be cost-effective options.
Implementing formal management processes and systems can improve efficiency. This might include adopting project management software or implementing regular performance reviews.
The Role of Support Networks and Infrastructure
Strong support networks and robust infrastructure are vital for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to thrive. These elements create a solid foundation for growth, fostering connections and enabling efficient operations.
Strengthening Supply Chains and Partnerships
SMEs can boost their growth by building resilient supply chains. This involves forging partnerships with reliable suppliers and leveraging data to optimise inventory management.
Key steps for strengthening supply chains include:
• Identifying trustworthy suppliers • Implementing real-time tracking systems • Diversifying supply sources to reduce risks
By collaborating with other businesses, SMEs can share resources and knowledge. This approach helps cut costs and improves efficiency across the supply chain.
Boosting Local Commerce and Community Networks
Local communities play a crucial role in supporting SME growth. Local government data initiatives can help businesses understand market trends and customer needs in their area.
SMEs can tap into community networks by:
• Participating in local business associations • Sponsoring community events • Offering apprenticeships or work placements
These actions help build a loyal customer base and attract skilled workers. They also contribute to the overall economic growth of the region.
Leveraging digital infrastructure, such as high-speed internet and cloud services, enables SMEs to reach wider markets and operate more efficiently.
Future Outlook for SMEs
The future for UK SMEs looks promising, with a focus on growth and innovation. Businesses are adapting to changing economic conditions and leveraging new technologies to stay competitive.
Predicting Trends in SME Growth
UK small businesses are prioritising growth initiatives for the coming years. Many firms plan to boost new business sales and reduce fixed costs. This approach aims to strengthen their financial position and expand market share.
The SME sector shows widespread optimism about future prospects. Industry experts anticipate a more positive economic climate in the near term. This outlook could lead to increased investment and job creation within small and medium-sized enterprises.
UK SMEs are expected to play a crucial role in driving economic recovery. Their agility and innovation capabilities position them well to adapt to market changes. As a result, the business population may see steady growth, contributing to overall economic stability.
Potential Innovations Shaping the Future of SMEs
Technology adoption is set to accelerate among SMEs. Artificial intelligence and machine learning tools could enhance operational efficiency and customer service. These innovations may help smaller firms compete more effectively with larger corporations.
Digital transformation will likely continue to be a key focus. E-commerce platforms and cloud-based solutions can enable SMEs to reach wider markets and streamline processes. This shift could lead to new business models and revenue streams.
Sustainability initiatives are gaining importance for SMEs. Green technologies and eco-friendly practices may become more prevalent. This trend could open up new opportunities in emerging sectors like renewable energy and circular economy solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The UK government provides various programmes and strategies to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These initiatives aim to boost growth, enhance digital capabilities, and improve management skills.
How can SMEs utilise the UK National Data Strategy to foster business expansion?
SMEs can leverage the UK National Data Strategy to drive growth. The strategy promotes data-driven innovation and encourages businesses to harness data for improved decision-making.
By adopting data analytics, SMEs can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour and market trends. This knowledge helps firms tailor their products and services to meet consumer needs more effectively.
What incentives does the UK government offer through the Help to Grow: Digital programme?
The Help to Grow: Digital programme offers SMEs financial support to adopt digital technologies. Eligible businesses can receive discounts on approved software solutions.
The programme aims to boost productivity and efficiency. It covers areas such as customer relationship management, digital accounting, and e-commerce platforms.
In what ways does the Help to Grow: Management course support SME development?
The Help to Grow: Management course equips SME leaders with essential business skills. It covers topics such as financial management, digital adoption, and marketing strategies.
Participants benefit from one-to-one mentoring and peer learning opportunities. The course helps SMEs develop actionable growth plans tailored to their specific needs.
What are the benefits for small businesses engaging with the Government Growth Guarantee Scheme?
The Government Growth Guarantee Scheme helps SMEs access finance for growth and expansion. It provides lenders with a government-backed guarantee on business loans.
This scheme enables SMEs to secure funding that might otherwise be unavailable. It supports a wide range of business activities, including investment in new equipment and hiring staff.
Can you outline the expected growth trends for UK SMEs in the coming years?
UK SMEs are showing positive growth trends despite economic challenges. Recent surveys indicate that many SMEs aim to increase sales in the next three years.
Digital adoption and innovation are key drivers of growth. SMEs that embrace new technologies and data-driven strategies are likely to see stronger performance.
How does the UK government classify the sizes of organisations for business support programmes?
The UK government uses specific criteria to classify business sizes for support programmes. These classifications are based on employee numbers and turnover.
Micro-businesses typically have fewer than 10 employees. Small enterprises employ 10-49 people, while medium-sized firms have 50-249 staff. These definitions help target support to businesses of different scales.