Public sector programs play a vital role in serving communities and addressing societal needs. These programs often face challenges in delivering services efficiently and effectively. Optimizing public sector programs can lead to improved outcomes, cost savings, and better use of resources.
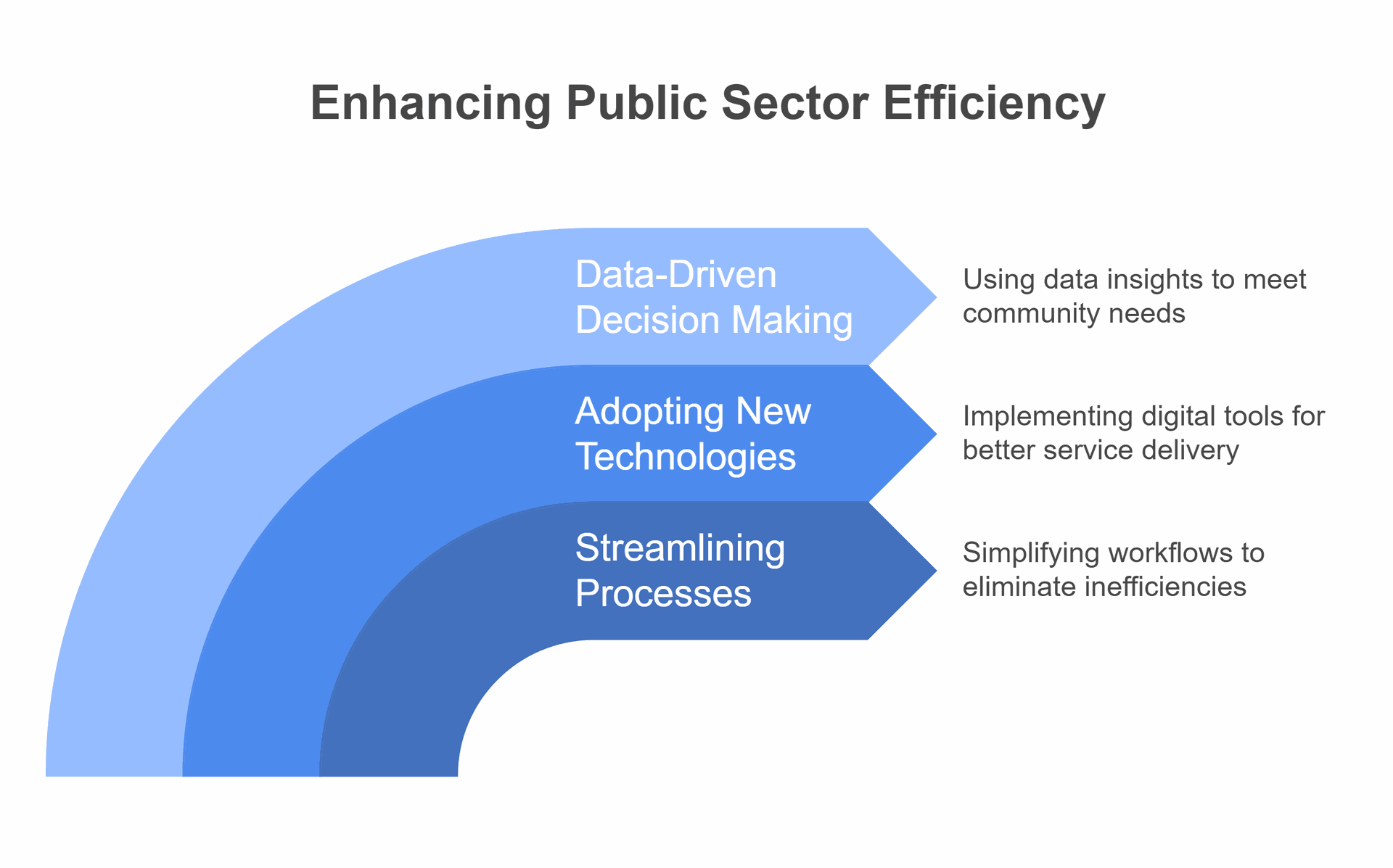
Governments and public agencies are exploring ways to enhance their operations and service delivery. This includes streamlining processes, adopting new technologies, and making data-driven decisions. By focusing on optimization, public sector organizations can do more with limited budgets and meet growing public expectations.
Process optimization in the public sector involves reviewing and refining existing workflows. This can help eliminate inefficiencies and reduce operational costs. It also allows agencies to adapt to changing needs and deliver services more effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Public sector optimization improves service delivery and resource utilisation
- Streamlining processes and adopting new technologies can enhance efficiency
- Data-driven decision-making helps public agencies meet community needs
Public Sector Programme Foundations
Public sector programmes form the backbone of government service delivery. They require careful planning, efficient execution, and continuous improvement to meet citizens' needs effectively.
The Role of the Public Sector in Service Delivery
The public sector plays a crucial role in providing essential services to citizens. These services span areas like healthcare, education, transportation, and social welfare.
Public organisations must balance quality and cost-effectiveness in their programmes. They face unique challenges, including budget constraints and political pressures.
Accountability is key in public service delivery. Agencies must show how they use taxpayer money to create value for communities.
Public service organisations are expected to enhance performance whilst improving efficiency. This dual focus shapes programme design and implementation.
Principles of Programme Optimisation
Programme optimisation in the public sector aims to maximise benefits with limited resources. It involves streamlining processes, reducing waste, and improving outcomes.
Key principles include:
- Clear goal-setting
- Data-driven decision making
- Stakeholder engagement
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation
Empowering teams is vital for successful programme optimisation. This involves giving staff the tools and authority to make improvements.
Effective governance structures ensure programmes stay aligned with organisational objectives. They also help manage risks and maintain transparency.
Innovation as a Catalyst for Efficiency
Innovation drives efficiency improvements in public sector programmes. It involves finding new ways to deliver services and solve complex problems.
Technology plays a major role in public sector innovation. Data analytics is predicted to have a significant impact on transforming government operations.
Innovative approaches in the public sector include:
- Digital service delivery
- Cross-agency collaboration
- Citizen co-creation of services
- Agile project management
Public leaders need to foster a culture of innovation. This involves encouraging creative thinking and being open to new ideas from all levels of the organisation.
Strategic Decision-Making in the Public Sector
Strategic decision-making shapes public sector programmes. It involves key factors like leadership, accountability and performance measurement. These elements work together to guide effective choices.
Frameworks for Enhancing Decision-Making Processes
Multicriteria analysis is a useful tool for public sector decision-making. It allows leaders to weigh multiple goals and use various data types.
Expert input can boost success rates. Studies show that when specialists take part, decisions tend to have better outcomes.
Data-driven approaches are vital. They help leaders make choices based on facts rather than gut feelings.
Stakeholder engagement is crucial. Getting input from those affected by decisions leads to more robust plans.
Risk assessment frameworks help spot potential issues early. This allows for proactive problem-solving.
The Impact of Leadership Style on Program Outcomes
Leadership style greatly affects public sector performance. Transformational leaders often drive innovation and change.
Transactional leaders focus on efficiency and following set rules. This can lead to steady, if not groundbreaking, results.
Servant leaders put staff needs first. This can boost morale and productivity.
Adaptive leadership helps navigate complex challenges. It's key for tackling new, unforeseen issues.
Collaborative leadership styles foster teamwork. This can lead to more creative solutions to public sector problems.
Accountability and Performance Measurement
Clear performance indicators are essential. They help track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Regular audits ensure transparency. They build public trust in government programmes.
Balanced scorecards offer a rounded view of performance. They look at financial, customer, internal process, and learning aspects.
Citizen feedback mechanisms are vital. They ensure services meet public needs.
Benchmarking against similar programmes helps set standards. It drives continuous improvement in public sector operations.
Fiscal Management and Optimisation
Effective fiscal management and optimisation are crucial for public sector programmes. These strategies help balance costs, quality, and efficiency while supporting economic recovery.
Cost Reduction and Budget Management
Public sector organisations face pressure to cut costs and manage budgets wisely. They often use methods like:
• Zero-based budgeting
• Activity-based costing
• Lean management techniques
These help identify areas for savings without hurting service quality.
Managers must review spending regularly. They should look for:
- Duplicated efforts
- Outdated processes
- Unnecessary expenses
Technology can help track spending in real-time. This lets teams spot issues quickly and make smart choices about where to trim.
Balancing Quality and Efficiency in Times of Financial Crisis
During a financial crisis, public services must do more with less. The key is to find ways to boost efficiency without lowering quality.
One approach is to focus on core services. Organisations can:
- Identify essential programmes
- Streamline processes
- Use resources more effectively
Public-private partnerships can also help. They bring in private sector expertise to improve service delivery.
Staff training is vital too. Well-trained employees can often find creative ways to maintain quality despite budget cuts.
Public Spending and Economic Recovery Strategies
Smart public spending can help drive economic recovery. Governments should focus on:
• Infrastructure projects
• Education and skills training
• Support for small businesses
These areas create jobs and boost long-term growth. Public finance management plays a key role in making sure money is spent wisely.
Targeted tax policies can also help. They can encourage investment and consumer spending.
It's important to balance short-term stimulus with long-term fiscal health. Governments must plan for future debt repayment while supporting current recovery efforts.
Operational Excellence in Public Sector Programs
Public sector programs can greatly benefit from operational excellence. By focusing on key areas, government agencies can improve efficiency and deliver better services to citizens.
Identifying and Addressing Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks in public sector programs often slow down service delivery. To tackle this issue, agencies must first pinpoint problem areas.
Common bottlenecks include:
- Outdated technology
- Lengthy approval processes
- Lack of staff training
Once identified, solutions can be implemented. For example, streamlining processes through automation can speed up workflows. Upgrading IT systems may also boost productivity.
Regular audits help spot new bottlenecks before they become major issues. This proactive approach keeps operations running smoothly.
Continuous Improvement and Incremental Optimisation
Continuous improvement is key to operational excellence in the public sector. It involves making small, ongoing changes to enhance service quality.
Steps for continuous improvement:
- Set clear goals
- Measure current performance
- Implement changes
- Assess results
- Repeat
Leveraging technology can aid this process. Data analytics tools help track progress and identify areas for optimisation.
Staff involvement is crucial. Encouraging employees to suggest improvements fosters a culture of innovation. Regular training keeps skills up-to-date and aligned with best practices.
Exploitation versus Exploration: Sustaining Ambidextrous Capacity
Public sector programs must balance exploitation of existing processes with exploration of new ideas. This ambidextrous approach ensures both efficiency and innovation.
Exploitation focuses on refining current operations. It involves:
- Fine-tuning existing services
- Maximising resource use
- Reducing waste
Exploration, on the other hand, seeks new opportunities. This may include:
- Piloting innovative programs
- Adopting emerging technologies
- Collaborating with external partners
Striking the right balance is key. Too much focus on exploitation can lead to stagnation. Excessive exploration may result in wasted resources. Adapting operational excellence models to fit existing structures helps maintain this balance.
Maximising Public Value through Optimised Services
Public sector organisations face the challenge of delivering high-quality services while managing limited resources. Effective optimisation strategies can help achieve both goals. Performance indicators, balanced cost-cutting, and strong leadership are key to maximising public value.
Utilising Performance Indicators in Service Delivery
Performance indicators play a crucial role in optimising public services. They provide measurable data to assess service quality and efficiency. Key metrics often include:
- Customer satisfaction ratings
- Response times
- Cost per service unit
- Number of people served
By tracking these indicators, agencies can identify areas for improvement. For example, a council might use wait times at local clinics to allocate staff more effectively.
Regular monitoring allows for quick adjustments. This improves the effectiveness of public services and helps generate more value for taxpayers' money.
Cost-Cutting Versus Service Quality Optimisation
Balancing cost reductions with service quality is a delicate task. Simply slashing budgets often leads to poorer outcomes. Instead, agencies should focus on smart optimisation.
Lean management techniques can streamline processes without compromising quality. For instance:
- Automating routine tasks
- Reducing paperwork
- Improving staff training
These approaches can cut costs while maintaining or even enhancing service levels.
It's vital to involve front-line staff in optimisation efforts. They often have valuable insights into where efficiencies can be found.
Advancing Public-Sector Leadership for Better Outcomes
Strong leadership is essential for successful service optimisation. Public-sector leaders must:
- Set clear goals and priorities
- Foster a culture of innovation
- Encourage cross-department collaboration
- Make data-driven decisions
Leaders should also focus on long-term value creation, not just short-term savings. This might involve investing in new technologies or staff development programmes.
Effective communication is crucial. Leaders need to explain the benefits of optimisation efforts to both staff and the public. This helps build support and reduces resistance to change.
By combining these leadership skills with a focus on public value, public-sector organisations can deliver better outcomes for their communities.
Organisational Strategies for Enhanced Public Services
Public sector organisations can boost their performance through targeted strategies. These approaches focus on fostering innovation, improving efficiency, and optimising specialised services.
Building Innovative Capacity within Public Service Organisations
Public service organisations (PSOs) are under pressure to innovate and improve performance. To build innovative capacity, PSOs can:
- Encourage idea-sharing among staff
- Create cross-functional teams
- Establish partnerships with external stakeholders
These methods help generate fresh ideas and solutions. PSOs should also invest in training programmes to enhance employees' skills in creative problem-solving.
A culture of innovation requires leadership support. Managers should reward innovative thinking and provide resources for experimentation. This approach can lead to more effective public services and increased citizen satisfaction.
Managerial Focus and Organisational Antecedents of Efficiency
Managers play a crucial role in driving efficiency within public sector organisations. They must:
- Set clear performance targets
- Implement robust monitoring systems
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement
Organisational structures significantly impact efficiency. Flatter hierarchies often lead to quicker decision-making and better communication.
Public sector organisations can enhance efficiency by:
- Streamlining processes
- Adopting technology solutions
- Encouraging employee feedback
Regular reviews of organisational procedures help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. By involving staff in these reviews, managers can tap into valuable frontline insights.
Regional Water Authorities and Specialised Service Optimisation
Regional water authorities offer a prime example of specialised service optimisation. These organisations can enhance their performance by:
- Implementing advanced water management technologies
- Developing data-driven decision-making processes
- Fostering collaborations with research institutions
By leveraging lean optimisation techniques, water authorities can reduce waste and improve service delivery. This might include automating routine tasks or redesigning customer service processes.
Training programmes for staff in water management best practices are essential. These initiatives ensure that employees have the skills to operate new technologies and implement innovative solutions.
Conclusions and Future Directions in Public Sector Research
Public sector research has made significant strides in recent years. It has shed light on ways to improve government services and operations.
One key area for future study is continuous improvement in public administration. Researchers should examine how agencies can foster a culture of ongoing enhancement.
Another crucial topic is the innovative capacity of public organisations. Studies could explore methods to boost creativity and implement novel solutions in government.
Future research should also focus on:
• Developing integrated theoretical frameworks
• Creating comprehensive models of public management
• Analysing the unique context of the public sector
• Enhancing methodological rigour in studies
These areas of inquiry can help drive meaningful reforms. They may lead to more efficient and effective public services.
Researchers should collaborate across disciplines to tackle complex challenges. Partnerships between academics and practitioners can yield valuable insights.
By pursuing these directions, public sector research can continue to evolve. It can provide vital knowledge to support government modernisation efforts worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Public sector programme optimisation involves various approaches, performance indicators, and technological solutions. Organisational culture and efficiency-enhancing methods also play crucial roles in improving government operations and service delivery.
What approaches can be taken to enhance the efficacy of public sector programmes?
Public sector organisations can improve their capabilities through technical assistance. This involves professional support in implementing projects and managing challenges.
Embracing data-driven insights and agile methodologies can create more responsive government operations. These approaches help in streamlining processes and improving service delivery.
Can you provide case studies illustrating successful public sector programme optimisation?
While specific case studies were not provided in the search results, many public sector organisations have successfully optimised their programmes.
These often involve implementing new technologies, streamlining processes, and improving citizen-centric services. Success stories typically showcase increased efficiency and better resource utilisation.
What are the key indicators of performance in the public sector?
Key performance indicators in the public sector often focus on service quality, efficiency, and effectiveness. These metrics help gauge the impact of optimisation efforts.
Public service performance (PSP) is a crucial measure. It reflects how well organisations are meeting their objectives and serving the public.
Which methods are most effective for eliminating waste and increasing productivity in government operations?
Process optimisation is a key method for improving government operations. It involves identifying inefficiencies and streamlining workflows.
Embracing technological innovations can significantly reduce waste and boost productivity. This might include automating repetitive tasks or implementing digital solutions.
In what ways can technology facilitate better outcomes in public sector service delivery?
Technology can enhance public sector service delivery in numerous ways. Digital platforms can improve access to services and information for citizens.
Data analytics can help organisations make more informed decisions. Automated systems can reduce processing times and minimise errors in service delivery.
How does organisational culture impact the optimisation of programmes within the public sector?
Organisational culture plays a vital role in programme optimisation. A culture that embraces innovation and continuous improvement is more likely to succeed.
Leadership support and employee engagement are crucial. When staff are motivated to seek efficiencies and improvements, optimisation efforts are more effective.