Public sector procurement plays a crucial role in the UK economy. It involves large sums of money and impacts various industries. The government spends billions each year on goods and services from external suppliers.
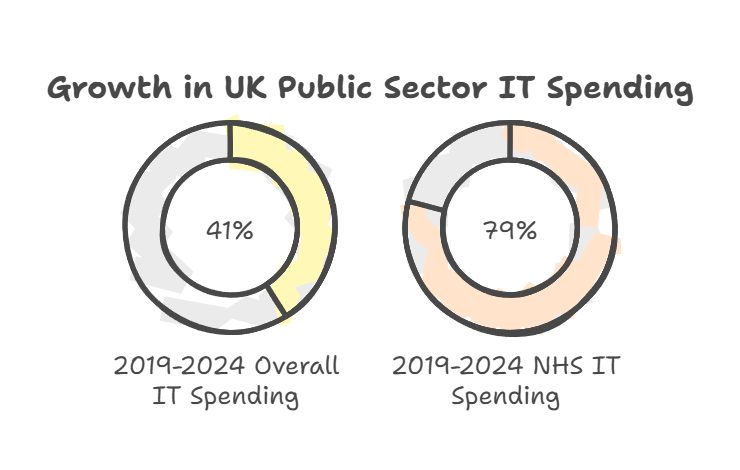
UK public sector spending on IT has increased by 41% between 2019 and 2024. This growth shows the rising importance of technology in government operations. The NHS, in particular, has seen a 79% increase in IT spending during this period.
Supplier collaboration is becoming more vital in public sector procurement. As budgets tighten and demands grow, working closely with suppliers helps organisations deliver better services and meet sustainability goals. This partnership approach is shaping the future of public sector supply chains.
Key Takeaways
- Public sector procurement accounts for a large portion of UK government spending
- IT spending in the public sector has grown significantly in recent years
- Collaboration between suppliers and public sector bodies is increasingly important
Overview of Public Sector Procurement
Public sector procurement plays a vital role in delivering essential services and managing government spending. It involves complex processes, key organisations, and strategic relationships that shape how public funds are used to benefit society.
Role of Procurement in Public Services
Procurement is crucial for ensuring efficient use of public funds and delivering quality services. It helps government bodies acquire goods and services needed to run smoothly. Public sector buyers must balance cost-effectiveness with social value and sustainability.
Key objectives include:
- Getting the best value for taxpayers' money
- Promoting fair competition among suppliers
- Supporting local economies and small businesses
- Meeting environmental and social goals
Effective procurement enables public services to operate efficiently and meet community needs. It covers a wide range of areas, from office supplies to major infrastructure projects.
Public Sector Organisations and Strategic Suppliers
Many public sector organisations rely on a core group of strategic suppliers for critical services. These suppliers work closely with government bodies to deliver essential functions.
Strategic suppliers are companies that do significant business with the government or provide vital services. The Cabinet Office takes a hands-on approach to managing these relationships.
There are currently 39 strategic suppliers in the UK. They span various sectors, including:
- IT and technology services
- Construction and infrastructure
- Healthcare and social care
- Defence and security
These suppliers often have long-term contracts and framework agreements with multiple public sector clients.
Regulatory Framework for Public Sector Procurement
UK public sector procurement operates within a complex regulatory framework. This ensures fairness, transparency, and value for money in government spending.
Key elements include:
- Public Contracts Regulations 2015
- Cabinet Office guidelines and policies
- Sector-specific rules (e.g. for NHS or defence)
Contracting authorities must follow specific procedures when tendering contracts above certain thresholds. These include open competition, clear evaluation criteria, and publication of contract notices.
The regulatory framework aims to prevent corruption and ensure equal opportunities for suppliers. It also promotes transparency, allowing public scrutiny of government spending decisions.
Financial Overview and Insights
Public sector suppliers must meet strict financial criteria. Transparency and accountability are key. Assessing financial health helps ensure reliable service delivery.
Assessing Financial Health of Suppliers
The public sector needs to evaluate suppliers' financial health. This process looks at key financial indicators. These include profit margins, debt levels, and cash flow.
A supplier's financial capacity affects their ability to deliver services. Strong finances mean a supplier can invest in staff and equipment. Weak finances might lead to service disruptions.
Public bodies use financial ratios to assess suppliers. These include:
- Liquidity ratio
- Profitability ratio
- Solvency ratio
Regular checks help spot potential issues early. This allows time for corrective action if needed.
Economic and Financial Standing (EFS) Criteria
EFS criteria help measure a supplier's financial stability. These criteria vary based on contract size and type. Common EFS factors include:
- Annual turnover
- Net assets
- Credit ratings
Public bodies set minimum thresholds for each factor. Suppliers must meet these to be considered for contracts. EFS assessments also look at past performance and future projections.
The goal is to find suppliers who can deliver over the long term. This helps prevent service disruptions and added costs.
Transparency and Accountability in Financial Reporting
Clear financial reporting is crucial in the public sector. It builds trust and allows for proper oversight. Suppliers must provide accurate, timely financial information.
The Whole of Government Accounts consolidates data from over 6,000 UK public sector organisations. This gives a broad view of public finances.
Key elements of transparent reporting include:
- Detailed income and expenditure statements
- Balance sheets showing assets and liabilities
- Cash flow statements
Regular audits help ensure accuracy. They also highlight areas for improvement in financial management.
Contract Management and Supplier Relationships
Managing contracts and building strong supplier relationships are crucial for public sector success. These practices help ensure value for money, mitigate risks, and foster innovation in public services.
Effective Contract Management Practices
Contract management is essential for maximising value from public sector agreements. It involves monitoring performance, addressing issues promptly, and ensuring suppliers meet their obligations.
The contract tiering tool helps prioritise contracts based on complexity and risk. High-value, strategic contracts require more intensive management.
Regular performance reviews and key performance indicators (KPIs) are vital. These metrics track supplier delivery against agreed standards.
Clear governance structures and escalation processes help resolve disputes quickly. This maintains smooth operations and positive relationships.
Building Resilient Supplier Relationships
Strong supplier relationships are key to navigating challenges in public sector procurement. Open communication and mutual trust form the foundation.
Regular supplier meetings foster collaboration and innovation. These sessions can identify improvements and address potential issues early.
Collaborative problem-solving during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, strengthens partnerships. It ensures continuity of essential services.
Recognising and rewarding excellent supplier performance encourages ongoing improvement. This can include performance-based incentives or contract extensions.
Crown Representatives and Supplier Engagement
Crown Representatives play a crucial role in managing relationships with strategic suppliers. They act as a bridge between government and key contractors.
These representatives work across multiple departments to ensure a consistent approach. They share best practices and coordinate supplier engagement.
The Sourcing Playbook guides Crown Representatives in effective supplier management. It provides tools and techniques for successful partnerships.
Regular supplier forums and industry days facilitate dialogue. These events help align supplier capabilities with government needs and foster innovation.
Strategies to Enhance Value and Efficiency
Public sector suppliers can boost their performance through smart procurement, cost modelling, and risk planning. These approaches help maximise value and streamline operations.
Procurement Strategies and Decision Making
Strategic procurement practices are key to improving efficiency in public sector buying. Suppliers should focus on:
- Bulk-buying and aggregation
- Transparent bidding processes
- Data-driven decision making
By aligning with government priorities, suppliers can offer better value for money. This may involve customising services or products to meet specific public sector needs.
Effective decision making relies on market research and understanding government objectives. Suppliers should stay informed about:
- Budget allocations
- Policy changes
- Departmental priorities
This knowledge helps tailor offerings and improve competitiveness in the bidding process.
Implementing Efficiency and Should-Cost Modelling
Efficiency in public procurement is crucial for both suppliers and buyers. Suppliers can enhance their value proposition by:
- Streamlining internal processes
- Adopting new technologies
- Improving supply chain management
Should-cost modelling helps suppliers understand the true costs of their products or services. This approach allows for:
- More accurate pricing
- Identification of cost-saving opportunities
- Better negotiation positions
By implementing these models, suppliers can offer competitive prices whilst maintaining profitability.
Risk Management and Resolution Planning
Effective risk management is essential for public sector suppliers. Key strategies include:
- Regular risk assessments
- Contingency planning
- Compliance monitoring
Suppliers should develop robust resolution plans to address potential issues quickly. This involves:
- Identifying critical services
- Establishing clear communication channels
- Creating step-by-step response procedures
By proactively managing risks, suppliers can build trust with public sector clients and ensure service continuity. This approach also helps protect reputations and maintain long-term relationships with government bodies.
Innovation and Sustainability in Public Sector Supply
Public sector organisations are leveraging their purchasing power to drive innovation and sustainability. These efforts aim to create positive change in supplier practices and broader societal impacts.
Fostering Innovation through Public Contracts
Innovation Public Procurement (IPP) is a key tool for transforming the economy towards green and digital solutions. Public bodies use contracts to encourage suppliers to develop new products and services.
IPP strategies include:
• Setting performance-based specifications
• Allowing alternative bids
• Establishing innovation partnerships
These approaches give suppliers flexibility to propose creative solutions. They also help public sector buyers access cutting-edge technologies and processes.
IPP benefits both buyers and suppliers. Buyers get better value and improved services. Suppliers gain opportunities to test and scale new ideas.
Integrating Sustainability and Social Value
Sustainable public procurement focuses on environmental, social, and economic impacts. It aims to influence supplier behaviour and create wider benefits.
Key elements include:
• Environmental criteria (e.g. carbon footprint, waste reduction)
• Social value requirements (e.g. local employment, fair wages)
• Lifecycle costing approaches
Public buyers are increasingly using their purchasing power to reshape markets. They set standards that encourage suppliers to adopt more sustainable practices.
This approach helps public organisations meet their own sustainability goals. It also drives positive change across supply chains and communities.
Specific Market Sectors Analysis
Public sector suppliers operate across diverse industries, each with unique challenges and opportunities. Key areas include construction, healthcare, and IT services, which play vital roles in the UK's infrastructure and public services.
Construction and Engineering Contracts
The construction and engineering sector is a major recipient of public sector contracts. Large-scale infrastructure projects often involve significant government spending. These contracts typically focus on:
- Transport infrastructure (roads, railways, airports)
- Public buildings (schools, hospitals, government offices)
- Energy facilities (power plants, renewable energy installations)
Public works projects aim to boost economic growth and improve public services. They often involve long-term partnerships between government bodies and private contractors.
Firms winning these contracts must demonstrate:
- Technical expertise
- Financial stability
- Strong project management skills
Healthcare Sector: Value for NHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is a massive purchaser of goods and services. It seeks suppliers who can provide:
- Medical equipment and supplies
- Pharmaceuticals
- IT systems for patient records and hospital management
- Facilities management services
Skill for Care, a charity offering skills training, received £117 million from health and education departments. This highlights the importance of workforce development in healthcare.
NHS procurement focuses on value for money and patient outcomes. Suppliers must offer innovative solutions that improve healthcare delivery while managing costs.
IT and Telecommunications: Cloud Computing Services
The public sector is increasingly relying on digital technologies. Cloud computing services are in high demand for:
- Data storage and management
- Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions
- Cybersecurity services
Government departments are moving towards cloud-based systems to improve efficiency and reduce costs. This shift creates opportunities for IT firms specialising in:
- Cloud migration
- Data analytics
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Suppliers in this sector must prioritise data security and compliance with government regulations. They should also focus on scalability and interoperability to meet the diverse needs of public sector clients.
Procurement Processes and Frameworks
Public sector procurement relies on structured processes and agreements to ensure efficient and fair supplier selection. These methods help manage costs and streamline purchasing across government organisations.
Understanding Framework Agreements
Framework agreements are key tools in public sector procurement. They establish terms for future contracts without committing to specific quantities. This allows buyers to quickly place orders as needed.
Framework agreements offer several benefits:
• Faster purchasing
• Reduced administrative costs
• Pre-vetted suppliers
• Bulk pricing discounts
Government buyers can use frameworks to purchase a wide range of goods and services. Common areas include IT, construction, and office supplies.
Suppliers must meet strict criteria to join a framework. This ensures high standards across all vendors. Once approved, suppliers can bid on relevant opportunities.
Pipeline Management and Pre-procurement
Pipeline management helps procurement teams plan future purchases. It involves tracking upcoming needs and market conditions. This process allows for better budgeting and resource allocation.
Key steps in pipeline management include:
- Identifying future requirements
- Assessing market capacity
- Estimating costs and timelines
- Prioritising projects
Pre-procurement activities lay the groundwork for successful purchasing. This phase focuses on research and preparation. Procurement teams gather data on potential suppliers and market trends.
Early supplier engagement is a crucial part of pre-procurement. It helps buyers understand supplier capabilities and innovations. This information shapes tender requirements and evaluation criteria.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Public Sector
Public sector suppliers face unique hurdles but can also find paths for growth. Key factors include outsourcing complexities and new avenues for expansion in government contracts.
Addressing Outsourcing Challenges
Outsourcing in the public sector brings both risks and rewards. Suppliers must navigate complex procurement rules and meet high standards. Local authorities often lack resources to manage large contracts effectively.
To succeed, suppliers should:
- Build strong relationships with government departments
- Understand specific agency needs and budgets
- Develop tailored solutions for public services
Resilience is crucial. Suppliers need robust systems to handle service disruptions and public scrutiny. Clear communication and transparency help build trust with government clients.
Exploring Opportunities for Growth
The public sector offers significant growth potential for suppliers. New procurement processes are creating more chances for businesses to engage with government buyers.
Key opportunities include:
- Digital transformation projects
- Sustainable and eco-friendly solutions
- Specialised consulting services
Suppliers can leverage data to identify upcoming contracts. By analysing past awards, they can spot trends and position themselves for future bids.
Innovation is highly valued. Suppliers who offer novel approaches to long-standing issues often gain an edge in competitive tenders.
Policy Impact and Future Outlook
Recent policy changes have reshaped public procurement. These shifts affect supplier relationships and contract terms. Future trends point to new ways of working with the public sector.
The Impact of Recent Policies on Public Procurement
The National Procurement Policy Statement has transformed UK public procurement. It applies to all contracting authorities, including central government departments.
New rules focus on transparency and value for money. Suppliers must now show how they'll deliver social value. This includes creating jobs and supporting local communities.
Public Contracts Regulations have been updated. They set stricter standards for bidding and contract management. Suppliers need to adapt to these changes quickly.
Future Trends Affecting Suppliers and Contracts
Digital transformation is reshaping procurement. E-procurement systems are becoming the norm. Suppliers must invest in technology to stay competitive.
Sustainability is a growing priority. Public sector buyers are looking for eco-friendly solutions. Suppliers who offer green alternatives will have an edge.
Contract lengths may change. Short-term agreements could become more common. This allows for flexibility in rapidly changing markets.
Data-driven decision making is on the rise. Suppliers will need to provide detailed performance metrics. Those who can't may lose out on contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Public sector supplier financial management involves complex factors and processes. Key aspects include stability metrics, performance reports, policy impacts, and due diligence procedures.
What factors influence the financial stability of strategic suppliers to the UK government?
Several elements affect supplier financial stability. Economic conditions play a major role. Changes in interest rates or inflation can impact costs and revenues.
Government spending levels also matter. Budget cuts may reduce contract values or volumes. This can strain suppliers' cash flows and profitability.
Regulatory changes can affect stability too. New rules might require costly compliance measures. This could squeeze profit margins for some suppliers.
How can one access detailed reports on the financial performance of public sector suppliers?
The UK government offers some public data on supplier performance. The Supplier Registration Service may provide financial information for registered companies.
Annual reports are available for larger public suppliers. These contain financial statements and performance data. Smaller private suppliers may not publish detailed reports.
Some third-party services offer financial analysis of public sector suppliers. These often require paid subscriptions to access full reports.
What metrics are utilised to evaluate the financial health of companies with public sector contracts?
Common financial health metrics include liquidity ratios. These measure a company's ability to pay short-term debts. The current ratio and quick ratio are examples.
Profitability ratios are also important. Gross profit margin and net profit margin show earnings relative to revenue. Return on assets indicates how efficiently a company uses its resources.
Debt ratios help assess long-term stability. The debt-to-equity ratio reveals how much a company relies on borrowing versus shareholder investment.
In what ways do changes in government procurement policies impact supplier finances?
New policies can affect payment terms. Faster payment practices may improve supplier cash flow. Delayed payments could cause financial strain.
Changes to contract insurance requirements can impact costs. Higher coverage limits might increase premiums, reducing profit margins.
Shifts in tender evaluation criteria can influence competitiveness. This may affect a supplier's ability to win contracts and maintain revenue.
How does market competition affect the financial positioning of strategic suppliers in the public sector?
Increased competition can pressure profit margins. Suppliers may need to lower prices to win contracts. This can impact their financial health.
Market consolidation might reduce competition. This could allow remaining suppliers to maintain higher margins. However, it may also increase scrutiny from procurement officials.
New market entrants can disrupt established suppliers. Innovative offerings might win contracts away from longstanding providers. This could affect their financial stability.
What are the procedures for conducting financial due diligence on potential public sector suppliers?
Financial due diligence often starts with a review of published accounts. This includes examining balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports.
Credit checks are common. These reveal payment history and creditworthiness. Poor credit scores may raise red flags about financial stability.
Some contracting authorities use financial health questionnaires. These ask suppliers to provide specific financial data and explanations.