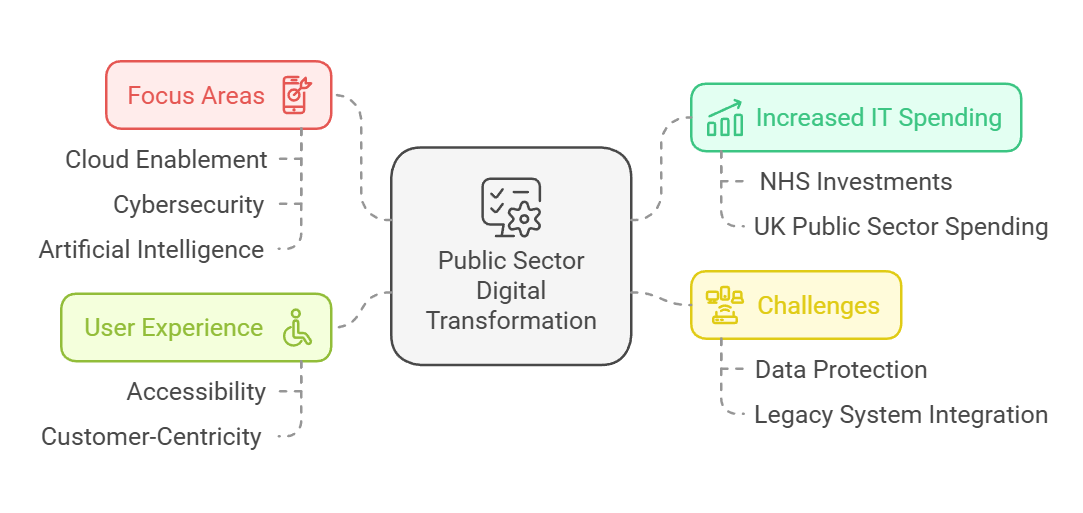
The public sector is embracing technology at an unprecedented rate. In recent years, UK public sector IT spending has surged by 41%, with the NHS alone increasing its tech investments by 79%. This shift towards digital solutions is reshaping how government services are delivered and accessed.
Public sector organisations are increasingly focusing on cloud enablement, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence to improve their operations and service delivery. These technologies offer opportunities for cost savings, enhanced efficiency, and better citizen engagement. However, the adoption of new tech also brings challenges, particularly in terms of data protection and legacy system integration.
As the public sector continues its digital transformation, there is a growing emphasis on user experience and customer-centricity. Government agencies are exploring innovative ways to make their services more accessible and user-friendly, often through pilot projects and emerging technologies. This approach aims to create a more responsive and efficient public sector that meets the evolving needs of citizens in the digital age.
Key Takeaways
- UK public sector IT investments are rapidly increasing, particularly in cloud, cybersecurity, and AI
- Digital transformation in government aims to improve service delivery and citizen engagement
- Public sector organisations face challenges in data protection and legacy system integration
Understanding Public Sector Technology
Public sector technology is rapidly evolving, bringing new tools and approaches to government services. These advancements are changing how agencies operate and serve citizens.
Evolution of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation in the public sector has come a long way. Governments now use online platforms to deliver services faster and more efficiently.
Many agencies have moved from paper-based systems to digital ones. This shift has made it easier for people to access information and complete tasks online.
UK public sector IT spending has grown by 41% in recent years. This shows a strong commitment to modernisation.
Digital transformation also includes updating old computer systems. New software helps staff work better and improves data security.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are changing how the public sector works. These technologies can process large amounts of data quickly.
Chatbots now answer common questions, freeing up staff for more complex tasks. AI also helps spot patterns in data, which can improve decision-making.
Government organisations are starting to see the benefits of AI. It can help predict needs, plan services, and even detect fraud.
Machine learning models get better over time. This means public services can keep improving as they learn from new data.
Impact of Cloud-Based Technology
Cloud technology has changed how the public sector stores and uses data. It offers more flexibility and can save money compared to old IT systems.
Agencies can now access powerful computing resources without owning all the hardware. This makes it easier to scale services up or down as needed.
Cloud systems also make it easier for different parts of government to work together. They can share data and collaborate on projects more easily.
Security is a top concern with cloud tech. But many cloud providers now offer strong protection for sensitive government data.
The Internet of Things in Public Services
The Internet of Things (IoT) is starting to make waves in public services. It connects everyday objects to the internet, creating 'smart' systems.
IoT in the public sector is a growing market. It's being used to make cities more efficient and improve public services.
Smart sensors can monitor air quality, traffic flow, and energy use. This data helps councils make better decisions about city planning.
In healthcare, IoT devices can track patient health at home. This could reduce hospital visits and improve care for people with long-term conditions.
While still new, IoT has the potential to transform how public services are delivered and managed.
User Experience and Customer-Centricity
Public sector organisations are putting citizens first. They are improving online services and making sure everyone can use them easily. This focus on the user is changing how government works.
Enhancing Digital Experience
Customer-centric government organisations build strategies around citizen needs. They study how people use services to find ways to make them better.
Many agencies are redesigning their websites and apps. They want them to be simple and quick to use. Some key improvements include:
• Clear language without jargon
• Mobile-friendly designs
• Personalised information based on user profiles
These changes help people find what they need faster. They also make it easier to complete forms and transactions online.
Focusing on Digital Literacy
As more services move online, digital skills become vital. Governments are working to boost these skills among citizens.
Some initiatives include:
• Free computer classes at libraries
• Online tutorials for e-government services
• Partnerships with schools to teach digital skills
The goal is to make sure everyone can use online services confidently. This helps both citizens and the government save time and money.
Accessibility and the Digital Divide
Not everyone has equal access to technology. This 'digital divide' can leave some people behind. Public sector organisations are trying to bridge this gap.
They are:
• Setting up free Wi-Fi in public spaces
• Offering low-cost internet plans for low-income families
• Creating accessible websites for people with disabilities
These efforts aim to make sure all citizens can benefit from digital services. It's a key part of making government truly customer-centric in the digital age.
Public Sector Organisations and Technologies
The UK public sector is embracing new technologies to improve services and efficiency. Digital innovations are transforming how government agencies, healthcare providers, and educational institutions operate and serve citizens.
Central and Local Government Innovations
Central and local governments are adopting emerging digital technologies to enhance public services. Artificial intelligence and blockchain are being used to streamline processes and increase transparency.
Many councils now offer online portals for residents to access services and information. These platforms allow citizens to pay council tax, report issues, and book appointments easily.
Central government departments are implementing cloud computing to improve data sharing and analysis. This enables more efficient policymaking and resource allocation across agencies.
Robotic process automation is being deployed to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up staff for more complex work. This technology is particularly useful in areas like benefits processing and licence applications.
Role of NHS in Digital Health
The NHS is at the forefront of digital health innovations in the UK. Electronic health records are improving patient care by providing healthcare professionals with quick access to medical histories.
Telemedicine services have expanded rapidly, allowing patients to consult with doctors remotely. This has improved access to healthcare, especially in rural areas.
The NHS App gives patients access to a range of services, including booking appointments and ordering repeat prescriptions. It also provides a secure way to view test results and medical records.
AI-powered diagnostic tools are being trialled to assist healthcare professionals. These systems can analyse medical images and help detect diseases earlier.
Wearable devices and health apps are being integrated into NHS care pathways. These tools help patients manage chronic conditions and provide valuable data to healthcare providers.
Technology Uptake in Education and Defence
In education, digital learning platforms are becoming commonplace. These systems allow students to access course materials, submit assignments, and collaborate with peers online.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are being used to create immersive learning experiences. This is particularly beneficial in subjects like science and history.
Schools are implementing digital safeguarding tools to protect students online. These systems monitor internet usage and flag potential safety concerns.
In the defence sector, advanced simulation technologies are enhancing military training. Virtual reality systems allow personnel to practice complex scenarios in a safe environment.
Cybersecurity is a top priority for defence organisations. Advanced technologies are being deployed to protect sensitive information and critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
The public sector faces unique challenges in protecting sensitive data and systems from cyber threats. Organisations must balance security needs with privacy regulations and operational demands.
Challenges in Cyber Security
Public sector entities often have complex IT infrastructures with many legacy systems. This makes them more vulnerable to attacks. Hackers target government data and services, seeking to disrupt operations or steal information.
Key threats include:
• Ransomware attacks
• Phishing scams
• Insider threats
• Supply chain compromises
Limited budgets and skills shortages compound these issues. Many agencies struggle to hire and retain cybersecurity talent.
To improve security, organisations should:
• Regularly update software and systems
• Train staff on security best practices
• Use strong authentication methods
• Implement network segmentation
Implementing GDPR and Data Privacy Measures
The UK public sector handles vast amounts of personal data. Protecting this information is crucial for maintaining public trust.
GDPR and UK data protection laws require strict safeguards. Key steps include:
- Data mapping and classification
- Privacy impact assessments
- Consent management
- Data minimisation
Agencies must also appoint Data Protection Officers. These experts guide compliance efforts and act as liaisons with regulators.
Technology plays a vital role in data protection. Encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention tools help secure sensitive information. Regular audits and testing ensure these measures remain effective.
Automation and Efficiency in the Public Sector
Technology is transforming how government agencies work. New tools help staff do more with less and serve the public better.
Integrating Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) uses software to handle repetitive tasks. This frees up staff for more complex work.
In the Australian Public Service, about 40% of employee time goes to data tasks. RPA can take over many of these jobs.
Government offices use RPA for:
• Data entry and validation
• Form processing
• Report generation
• Employee onboarding
RPA speeds up work and cuts errors. It also improves job satisfaction by reducing dull tasks.
Some agencies worry about job losses. But RPA often leads to staff moving to more rewarding roles.
Leveraging AI for Automation and Predictive Policing
AI helps automate complex processes in government. It can spot patterns humans might miss.
Fraud detection is one key use. AI analyses data to flag suspicious activity in benefits or tax systems.
Predictive policing uses AI to guide patrols. It looks at crime data to suggest high-risk areas.
AI can also:
• Answer citizen queries 24/7
• Predict maintenance needs for infrastructure
• Optimise traffic flow in cities
Ethical concerns exist around AI use. Bias in data or algorithms can lead to unfair outcomes.
Governments must balance AI's benefits with privacy and fairness concerns.
Innovation through Pilot Projects and Emerging Technologies
The public sector is embracing new technologies to improve services and operations. Blockchain, 5G, and virtual reality are key focus areas driving innovation and efficiency gains.
Blockchain for Transparency and Security
Blockchain technology is transforming public sector recordkeeping and transactions. Government agencies are piloting blockchain projects to enhance transparency and security.
Land registries are testing blockchain to create tamper-proof property records. This reduces fraud and speeds up property transfers.
Tax authorities use blockchain to track payments and combat tax evasion. The distributed ledger provides an unalterable audit trail.
Blockchain-based voting systems are being trialled to increase election integrity. These systems offer better security and auditability than traditional methods.
Exploring 5G and Digital Connectivity
5G networks promise ultra-fast speeds and low latency for public services. Cities are partnering with telecoms to test 5G applications.
Smart traffic management systems use 5G to collect real-time data from sensors and vehicles. This allows dynamic traffic light control to reduce congestion.
Emergency services benefit from 5G's high bandwidth for video streaming and file transfers. Paramedics can send high-quality images to hospitals en route.
Remote areas gain better access to e-government services through 5G fixed wireless. This narrows the digital divide between urban and rural communities.
Virtual Reality for Training and Services
Virtual reality (VR) creates immersive environments for public sector training and service delivery. Government agencies are piloting VR projects in various fields.
Police forces use VR simulations to train officers in de-escalation techniques. This improves decision-making in high-stress situations.
Healthcare providers employ VR for surgical training. Doctors practise complex procedures in a risk-free virtual setting.
Museums offer virtual tours to increase accessibility. Visitors explore exhibits remotely, boosting engagement with cultural heritage.
Social services use VR to help people with disabilities practise life skills. Virtual environments provide safe spaces for learning and development.
Digital Infrastructure and Investments
Digital infrastructure and smart investments are reshaping public services. Governments are embracing technology to improve efficiency and build connected cities.
Progressing Towards Smart Cities
Smart cities use digital tech to enhance urban life. They connect systems like transport, energy, and waste management. This improves services and saves money.
Digital public infrastructure (DPI) is key to smart city growth. It includes things like digital ID systems and payment platforms.
Smart traffic lights adjust to real-time conditions. This cuts jams and pollution. Smart bins alert when they need emptying. This makes waste collection more efficient.
Data from these systems helps leaders make better choices. They can spot trends and fix problems faster.
Investment in Technology and GovNet
Governments are spending more on tech. In 2022, market sector investment in digital infrastructure reached £9.2 billion in the UK.
GovNet is a secure network for public services. It lets different parts of government share data safely. This helps provide better, joined-up services.
Investing in tech skills is vital. Governments need staff who can use new tools well. They're hiring tech experts and training current workers.
Cloud computing is a big focus. It lets agencies access powerful tech without huge upfront costs. This makes it easier to try new ideas.
Strategic Approach to Procurement and Partnerships
Public sector organisations are adopting new strategies for procurement and partnerships. These approaches aim to boost innovation and efficiency.
One key trend is the rise of public-private partnerships. These collaborations bring together government bodies and private companies. They often lead to fresh ideas and improved services.
Procurement teams are also embracing technology. Digital tools help them make smarter decisions. For example, some use data analytics to assess suppliers and costs.
Benefits of strategic procurement:
• Better value for money
• Increased innovation
• Improved supplier relationships
• More efficient processes
Flexible procurement methods are gaining popularity. These allow public bodies to adapt quickly to changing needs. They can test new ideas without long-term commitments.
Many organisations now focus on long-term value rather than just price. This shift encourages suppliers to offer innovative solutions. It also promotes sustainable practices.
Strategic partnerships are becoming more common. These involve close collaboration between buyers and suppliers. They often lead to joint problem-solving and shared goals.
By taking a strategic approach, public sector bodies can drive positive change. They can deliver better services while making the most of limited resources.
Challenges and Solutions for Legacy Systems
Legacy systems pose major hurdles for public sector organisations. These outdated technologies hinder efficiency and innovation. Modernising them is crucial but complex.
Digital Upgrades and Cloud Migration
Many government agencies struggle with legacy technology barriers. These old systems are costly to maintain and often can't meet modern needs.
Digital upgrades offer a way forward. Replacing outdated hardware and software with newer solutions can boost performance and security.
Cloud migration is another key strategy. Moving data and applications to the cloud can improve flexibility and reduce costs. It also allows for easier updates and scaling.
Legacy systems often use outdated programming languages. This makes finding skilled staff to maintain them difficult.
Modernisation isn't just about new tech. It requires changes in processes and culture too. Staff training is essential for smooth transitions.
Phased approaches can help manage risks. Organisations might start by moving less critical systems first. This allows for learning and adjustment before tackling core operations.
Data Management and Quality
Data management and quality are essential for effective public sector operations. These practices ensure information is reliable, accessible, and useful for decision-making.
Importance of Data Quality and Management
Good data quality is crucial for government agencies. It helps them make better choices and serve citizens more effectively. Poor quality data can lead to bad results, even when using advanced systems.
Data management involves organising, storing, and protecting information. This process is vital as governments hold vast amounts of data. The European Data Portal, for example, has over 1.1 million datasets from EU countries.
Quality checks are key to data management. They ensure information is accurate and up-to-date. This is especially important when using new tech like AI and machine learning.
Good data practices can save money and improve services. They help spot trends and solve problems faster. Data and analytics could create £940 billion in value for the public sector each year if used well.
Future Trends in Public Sector Technology
The public sector is rapidly embracing new technologies to improve services and efficiency. Key areas of focus include digital transformation, remote work solutions, and emerging tech like artificial intelligence.
Predicting Technology Trends in Public Sector
Artificial intelligence (AI) adoption is set to accelerate in public services. AI will analyse large datasets to provide insights and enable personalised user experiences.
Cloud computing will continue to grow, allowing for more flexible and scalable government IT systems. This shift supports remote work and improves service delivery.
Cybersecurity will remain a top priority. As digital services expand, protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure becomes even more crucial.
Blockchain technology may see increased use for secure record-keeping and transparent transactions.
The Internet of Things (IoT) will help create smarter cities. Connected devices will improve urban planning, traffic management, and public utilities.
Virtual and augmented reality could enhance training and education in public sector roles.
Remote Working and Public Sector Operations
The public sector has rapidly adapted to remote work, leveraging technology to maintain services. This shift has brought both challenges and opportunities for government agencies and workers.
Adapting to Remote Work Challenges
Remote working in the public sector became essential during the pandemic. Agencies had to quickly provide staff with the necessary tools and secure access to work from home.
This transition revealed several challenges:
- Ensuring data security and confidentiality
- Maintaining team collaboration and communication
- Adapting workflows and processes for virtual environments
Despite these hurdles, many public sector organisations found remote work beneficial. It offered flexibility and potential cost savings through estate rationalisation.
To support remote workers, governments developed checklists covering:
- IT equipment and secure access
- Virtual meeting platforms
- Digital document management systems
Digital Services for Remote Working
Public sector technology played a crucial role in enabling remote operations. Cloud systems became essential for seamless access to data and applications.
Key digital services implemented include:
- Virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure connections
- Cloud-based collaboration tools
- Digital signatures and approval processes
These technologies not only supported remote work but also improved service delivery to citizens. Many government agencies expanded their online services, reducing the need for in-person visits.
The shift to digital also highlighted the importance of cybersecurity. Public sector organisations invested in robust security measures to protect sensitive data accessed remotely.
Towards a Digital Future: Final Thoughts
The public sector is rapidly embracing digital transformation. Government organisations are increasingly adopting cloud enablement and cyber security measures to enhance their technological capabilities.
Public cloud systems are playing a crucial role in this shift. These systems offer scalability and flexibility, allowing government agencies to adapt quickly to changing needs.
Cloud services provide numerous benefits:
• Cost-effective solutions • Improved data storage and management • Enhanced collaboration between departments • Increased accessibility for citizens
Despite progress, challenges remain. Cybersecurity concerns and data privacy issues must be addressed to ensure public trust in digital government services.
The Home Office's Product Lifecycle Management initiative exemplifies a collaborative approach. It brings together policy, operations, and technology skills to design and deliver effective digital solutions.
As governments continue to invest in digital infrastructure, citizen engagement will likely improve. Online services, mobile applications, and AI-powered chatbots are becoming commonplace, streamlining interactions between the public and government agencies.
The future of public sector technology looks promising. With continued focus on innovation and digital literacy, governments can create more efficient, responsive, and citizen-centric services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Public sector technology is rapidly evolving, driving changes in service delivery, operational efficiency, and citizen engagement. Key frameworks and events are shaping the landscape, while innovative approaches contribute to government modernisation.
How is technology transforming services in the public sector?
Technology is improving customer and user experience in public services. Digital tools enable faster, more accessible services for citizens. Online portals and mobile apps allow people to access information and complete transactions 24/7.
Data analytics help agencies make better decisions and target resources more effectively. Artificial intelligence is being used to automate routine tasks, freeing up staff for more complex work.
What are the leading frameworks guiding technology implementation in the public sector?
The UK government's Digital Service Standard provides guidelines for building user-centred digital services. It emphasises understanding user needs, using agile methods, and continuous improvement.
The ITIL framework offers best practices for IT service management in the public sector. It helps organisations align IT services with business needs and improve service quality.
Which are the key public sector technology events scheduled for 2024?
Digital Government 2024 will take place in London, focusing on digital transformation strategies. The Public Sector ICT Summit is set for Manchester, covering emerging technologies in government.
GovTech 2024 in Edinburgh will showcase innovative solutions for public services. CyberUK 2024 in Cardiff will address cybersecurity challenges for government organisations.
How is public sector innovation contributing to government efficiency?
Cloud computing is helping agencies save time and money. It allows for more flexible and scalable IT infrastructure, reducing costs and improving service delivery.
Robotic process automation is streamlining administrative tasks, cutting processing times and reducing errors. This frees up staff to focus on more valuable work serving citizens.
What are the objectives driving the digitisation of public sector services?
Improving accessibility is a key goal, making services available to more people through digital channels. Enhancing efficiency aims to reduce costs and speed up service delivery.
Increasing transparency is another objective, with open data initiatives providing more information to the public. Personalisation of services is also a focus, tailoring interactions to individual needs.
How does Public Technology support the advancement of government operations?
Public Technology helps streamline policy-making and citizen engagement. It enables better data collection and analysis for informed decision-making.
Digital platforms facilitate more efficient communication between government agencies and the public. This improves responsiveness and helps build trust in public institutions.