Local authorities across the UK are facing increasing pressure to deliver high-quality services while managing tight budgets. Regional procurement trends play a crucial role in achieving this balance. Local government spending now exceeds £70 billion annually, making strategic procurement practices more important than ever.
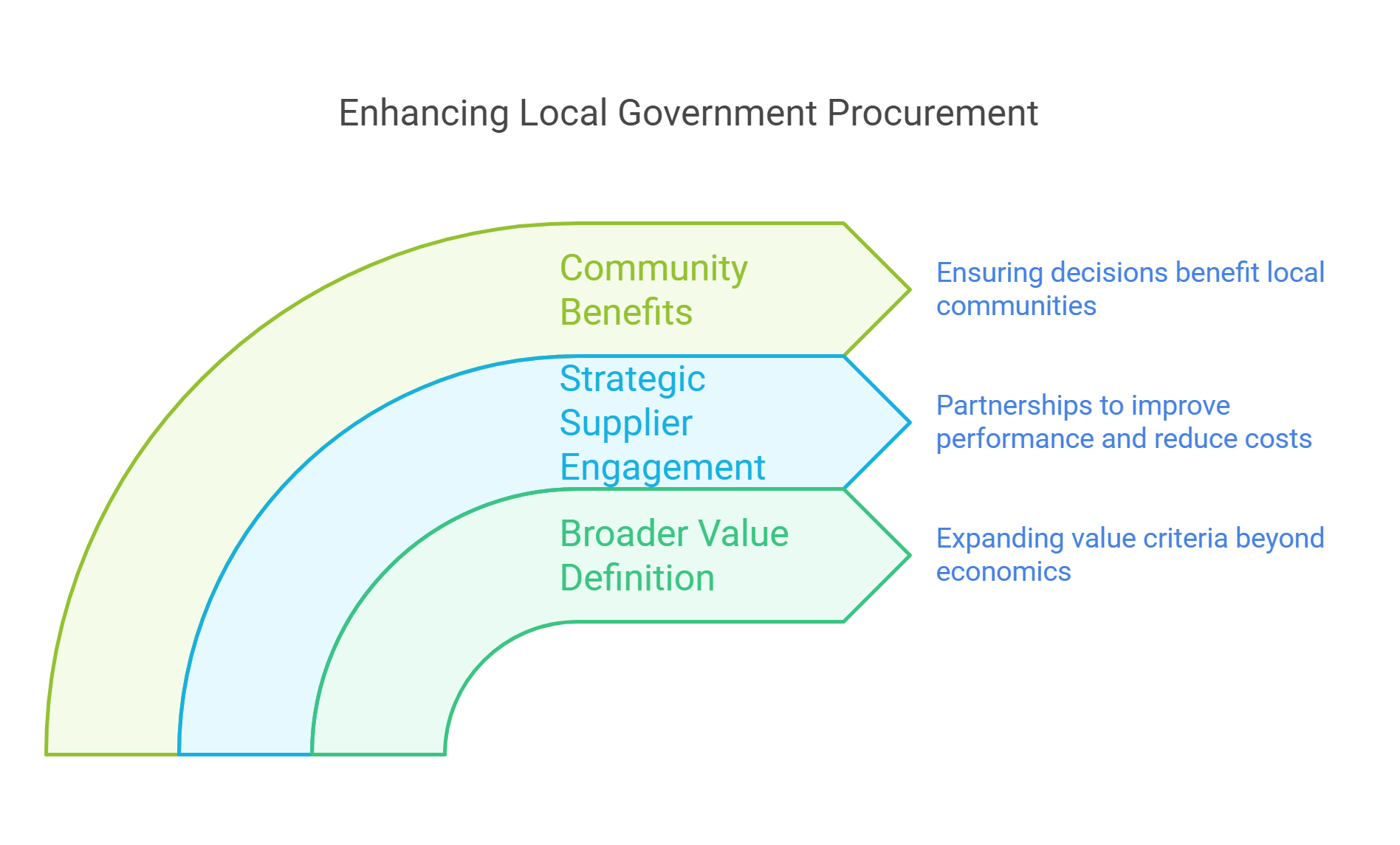
These trends are shifting towards a broader definition of value. The focus is moving away from purely economic considerations to include social and environmental factors. This change allows councils to make more well-rounded decisions that benefit their communities in multiple ways.
Engaging with strategic suppliers is becoming a key part of regional procurement strategies. Local authorities are working to improve performance, reduce costs, and drive innovation through these partnerships. This approach helps create a more dynamic and responsive procurement process.
Key Takeaways
- Regional procurement trends prioritise broader value beyond economic factors
- Strategic supplier engagement is crucial for improving performance and reducing costs
- Local authorities are adapting procurement strategies to benefit their communities
Overview of Local Government Procurement
Local government procurement plays a vital role in delivering public services and achieving value for money. It involves complex processes, legal requirements, and strategic decision-making by councils across the UK.
Public Procurement Fundamentals
Public procurement refers to the purchase of goods, services, and works by government bodies. For local authorities, this process is guided by strict rules and regulations.
Key principles include:
- Transparency
- Fairness
- Value for money
- Competition
Local authorities in England spend about £82.4 billion yearly on goods and services. This represents a significant portion of public spending.
Procurement methods vary based on the value and nature of contracts. These may include open tenders, framework agreements, and dynamic purchasing systems.
The Role of Councils in Procurement
Councils are responsible for purchasing a wide range of goods and services. These can include:
- Construction projects
- Waste management
- Social care services
- IT systems
The National Procurement Strategy aims to help councils deliver both economic and social value to their communities. This strategy emphasises the importance of sustainable and ethical procurement practices.
Councils must balance cost-effectiveness with broader community benefits. This includes supporting local businesses and promoting environmental sustainability.
Understanding the Procurement Act
The Procurement Act 2023 introduces significant changes to public procurement in the UK. These changes aim to simplify processes and increase flexibility for buyers.
Key features of the Act include:
- A single regulatory framework
- New procedures for awarding contracts
- Increased transparency requirements
The Act comes into force in just over four months, requiring councils to adapt their procurement practices.
It emphasises value for money and social value considerations. This aligns with the broader goals of local government procurement to benefit communities.
Strategies for Local Authorities
Local authorities can use smart procurement tactics to boost efficiency and deliver better public services. These methods focus on effective commissioning, well-planned strategies, and adding social value to contracts.
Commissioning for Public Services
Commissioning helps local authorities get the most from their spending. It's about planning and buying services that meet local needs. Good commissioning looks at the whole picture, not just cost.
Local councils should:
• Talk to residents about what they need • Work with other organisations to share ideas • Look for new ways to solve problems • Check if services are working well
Smart commissioning can lead to better services and save money. For example, some councils have joined up health and social care. This helps people and cuts costs.
Local Government Procurement Strategy
A strong procurement strategy guides how councils buy goods and services. It sets out clear goals and ways to reach them. The strategy should fit with the council's bigger plans.
Key parts of a good strategy:
• Clear targets for saving money • Plans to support local businesses • Ways to use technology to make buying easier • Rules to make sure spending is fair and open
Councils should review their strategy often. This helps them keep up with changes and new ideas.
Incorporating Social Value
Social value means getting extra benefits from council spending. It's about more than just buying things. It's about making life better for local people.
Ways to add social value:
• Asking suppliers to hire local workers • Buying from small, local businesses • Choosing eco-friendly options • Getting contractors to support community projects
The Social Value Act says councils must think about social value when they buy services. This helps make sure public money does more good.
Supplier Engagement and Management
Local authorities can improve procurement outcomes by building strong supplier relationships, managing contracts effectively, and fostering innovation. These strategies help create value and drive efficiency in public spending.
Fostering Relationships with Local Suppliers
Building strong ties with local suppliers is crucial for regional economic growth. Local government remains a significant purchaser at both place and aggregate levels. Councils can support small businesses by:
- Hosting supplier engagement events
- Providing clear guidance on bidding processes
- Offering prompt payment terms
By nurturing these relationships, authorities can tap into local expertise and create jobs. This approach also helps build resilient supply chains that can withstand disruptions.
The Complexities of Contract Management
Effective contract management ensures value for money and high-quality service delivery. Key aspects include:
- Regular performance reviews
- Clear communication channels
- Risk assessment and mitigation
Strategic supplier management is becoming increasingly important. Councils should develop programmes to engage with key suppliers at both local and national levels. This helps resolve issues quickly and identifies opportunities for improvement.
Promoting Innovation among Suppliers
Encouraging innovation in the supply chain can lead to better services and cost savings. Local authorities can:
- Set innovation-focused procurement criteria
- Organise 'innovation days' with suppliers
- Offer incentives for new ideas
By creating an environment that values creativity, councils can benefit from cutting-edge solutions. This approach also helps suppliers stay competitive and grow their businesses.
Embracing digital tools can streamline procurement processes and improve supplier engagement. Authorities should consider implementing e-procurement systems to enhance efficiency and transparency.
Impact on Local Economies and Communities
Local authority procurement practices can significantly shape economic outcomes and community wellbeing. Strategic purchasing decisions have the potential to stimulate growth, create jobs, and support social enterprises.
Economic Growth through Procurement
Local procurement can act as a catalyst for economic development. When local authorities direct spending towards area businesses, it keeps money circulating within the community. This multiplier effect boosts local economic activity.
Targeted procurement also helps diversify the local economy. By supporting a range of sectors, authorities reduce reliance on a single industry. This builds economic resilience.
Procurement policies can encourage innovation too. When local firms compete for contracts, it drives them to improve products and services. This enhances their competitiveness beyond the local market.
Procurement as an Anchor for Job Creation
Strategic procurement creates employment opportunities. When local businesses win contracts, they often need to hire more staff. This reduces unemployment and increases household incomes in the area.
Local authority spending can also support specific job sectors. For example, construction contracts create roles in the building trade. IT services procurement boosts tech sector employment.
Procurement can be used to target unemployment hotspots. By choosing suppliers from deprived areas, authorities help create jobs where they're most needed.
Empowering Social Enterprises
Procurement policies can nurture social enterprises. These organisations combine business practices with social goals. By winning contracts, they gain financial stability and grow their impact.
Local authorities can set aside a portion of contracts for social enterprises. This helps them compete against larger firms. It also ensures public spending delivers community benefits.
Social value clauses in contracts encourage all suppliers to consider their wider impact. This might include creating apprenticeships or using environmentally friendly practices. Such requirements help spread social enterprise values across the economy.
Leadership and Capacity Building
Effective leadership and capacity building are crucial for local authorities to enhance their procurement practices. These elements foster innovation, efficiency, and value creation in regional procurement.
Leadership in Public Procurement
Strong leadership is essential for driving strategic procurement initiatives. Procurement leaders in local authorities must set clear visions and goals. They should champion best practices and inspire their teams to achieve excellence.
Leaders need to advocate for procurement's strategic role within the organisation. This involves engaging with senior management and elected officials. They must also promote transparency and ethical standards in all procurement activities.
Effective leaders foster a culture of continuous improvement. They encourage their teams to seek innovative solutions and embrace new technologies. By doing so, they position procurement as a value-adding function rather than a mere administrative process.
Resource Management and Expertise Development
Local authorities must invest in their procurement teams' skills and knowledge. This involves providing regular training and professional development opportunities. Procurement experts need to stay updated on market trends, legal requirements, and best practices.
Resource allocation is crucial. Authorities should ensure adequate staffing and tools for effective procurement. This may include specialised software for contract management and spend analysis.
Developing internal expertise is vital. Authorities can create mentorship programmes and knowledge-sharing platforms. These initiatives help retain institutional knowledge and build a skilled procurement workforce.
Collaborative Approaches and Good Practice
Collaboration between local authorities can lead to significant benefits. Shared procurement services and joint contracts can yield economies of scale. They also allow for the exchange of knowledge and best practices.
Authorities should actively participate in procurement networks and forums. These platforms enable the sharing of successful strategies and lessons learned. They also provide opportunities for benchmarking and continuous improvement.
Adopting good practice involves learning from both public and private sector examples. This can include implementing category management approaches or utilising e-procurement systems. Regularly reviewing and updating procurement processes ensures they remain effective and efficient.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
Local authorities in England face a complex landscape of rules and regulations when it comes to procurement. Recent changes aim to give councils more flexibility while ensuring value for money.
Navigating National and Local Legislation
The public sector procurement rules in England are changing. Central government is moving from "most economically advantageous tender" to "most advantageous tender". This shift allows councils to focus on broader value beyond just cost.
Local authorities must balance national guidelines with their own policies. Many councils have sustainability targets that influence purchasing decisions. Some prioritise local suppliers to boost the regional economy.
Procurement teams need to stay up-to-date on both national and local rules. Regular training helps staff navigate this complex environment.
The Impact of the Procurement Bill
The new Procurement Bill aims to simplify and speed up the purchasing process. It gives local authorities more freedom to design their own procedures.
Key changes include:
- Replacing EU-derived regulations with a single UK framework
- Allowing more consideration of social value in contract awards
- Streamlining processes for lower-value contracts
The bill also introduces new transparency requirements. Councils will need to publish more information about their contracts and suppliers.
These changes offer opportunities but also challenges. Procurement teams will need to adapt their practices to comply with the new rules.
Local Authority Self-Assessment
Self-assessment tools help councils evaluate their procurement practices. These assessments cover areas like strategy, skills, and supplier relationships.
Regular self-assessments allow authorities to:
- Identify strengths and weaknesses
- Benchmark against other councils
- Set improvement targets
Many councils use the National Procurement Strategy toolkit. This provides a framework for assessing capability across key themes.
Self-assessment results can inform training plans and process improvements. They also help councils demonstrate good governance to auditors and the public.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Local authorities are adopting sustainable and ethical procurement practices to create positive environmental and social impacts. These efforts focus on reducing carbon emissions, supporting local economies, and ensuring responsible business practices throughout supply chains.
Advancing Sustainability in Procurement
Sustainable procurement aims to meet organisational needs while minimising environmental damage and generating benefits for society and local economies. Local authorities are increasingly considering whole-life costs and impacts when making purchasing decisions.
Key strategies include:
• Setting sustainability criteria in tenders • Prioritising energy-efficient products and services • Reducing waste through circular economy principles • Sourcing from local suppliers to cut transport emissions
Many councils now require suppliers to report on their carbon footprint and set emissions reduction targets. This helps track progress towards climate goals and drives innovation in low-carbon goods and services.
Managing Strategic Risk
Strategic risk management in procurement helps local authorities navigate uncertainties and protect their operations. Key risks include:
• Supply chain disruptions • Cybersecurity threats • Regulatory changes • Reputational damage from unethical suppliers
To mitigate these risks, councils are:
• Diversifying supplier bases • Conducting thorough due diligence on contractors • Improving contract management processes • Developing contingency plans for critical supplies
Regular risk assessments and supplier audits help identify potential issues early. Building strong relationships with key suppliers also improves resilience and allows for collaborative problem-solving.
Corporate Social Responsibility in Procurement
Local authorities are using procurement to drive positive social outcomes and support responsible business practices. This includes:
• Promoting fair labour standards and living wages • Supporting diversity and inclusion among suppliers • Encouraging apprenticeships and local job creation • Ensuring ethical sourcing of materials
Many councils now include social value criteria in their tender evaluations. This might involve scoring suppliers on their community engagement or employment practices.
Councils are also working to eliminate modern slavery from supply chains. This involves rigorous supplier vetting and clauses in contracts requiring ethical labour practices.
Trends and Innovations
Local authorities are embracing new approaches to procurement. These changes aim to boost efficiency, cut costs, and improve services. Key areas of focus include emerging trends, process improvements, and digital tools.
Emerging Trends in Local Authority Procurement
Encouraging innovation is a top priority for local government procurement. Authorities are looking beyond price to find creative solutions. They're asking suppliers for fresh ideas to tackle complex issues.
Sustainability is gaining importance. Many councils now consider environmental impact in their buying decisions. This includes factors like carbon footprint and waste reduction.
Collaboration between authorities is on the rise. Shared procurement helps leverage buying power and reduce costs. It also allows smaller councils to access better deals.
Risk management is becoming more sophisticated. Authorities are developing strategies to handle supply chain disruptions and market volatility.
Innovations in Procurement Process
The procurement landscape is changing rapidly. New laws aim to simplify and speed up the buying process. The Procurement Act introduces several key benefits for local authorities.
E-procurement systems are becoming standard. These platforms streamline the tendering process and improve transparency. They make it easier for small businesses to bid for contracts.
Outcome-based procurement is gaining traction. This approach focuses on results rather than specific goods or services. It gives suppliers more freedom to innovate.
Agile procurement methods are being adopted. These allow for more flexibility and faster decision-making. They're especially useful for complex or evolving projects.
Digital Transformation and Data Analysis
Technology is reshaping local authority procurement. Artificial intelligence is being used to analyse spending patterns and identify savings. It can also help predict future needs and market trends.
Big data analytics are improving decision-making. Authorities can now track supplier performance in real-time. This helps them make informed choices and manage risks better.
Blockchain technology is being explored for secure, transparent transactions. It could revolutionise contract management and payment processes.
Cloud-based procurement systems are becoming more common. They offer greater flexibility and easier access to information. This is especially useful for remote working and collaboration between teams.
Social Care and Health Integration
The integration of social care and health services aims to improve outcomes for people. It involves joint planning and delivery of care. This approach can lead to better use of resources and more coordinated support.
Procurement in Health and Social Care
Health and social care procurement is changing. Local authorities now consider the Care Act 2014 and Children and Families Act 2014 when buying services. They focus on getting value for money and meeting people's needs.
Councils use new tools to buy care services. These help them follow rules and find good providers. Many now look at the whole cost of care, not just the price.
Integrated Care Boards (ICBs) play a big role. They work with councils to plan and buy health and care services together.
Creating Value in Social Care Procurement
The Public Services (Social Value) Act 2012 changed how councils buy services. They must think about the social, economic and environmental benefits of their purchases.
In social care, this means looking at:
- How services help people stay independent
- Ways to support local jobs and businesses
- Ideas to reduce environmental impact
Councils now ask care providers to show how they add value. This could be by training staff or working with community groups.
Some areas use 'social value calculators' to measure benefits. This helps them choose providers that offer the most value.
Collaboration Between Health Bodies and Local Authorities
Health and social care integration is a key goal. NHS bodies and councils are working closer together. They share budgets and plan services jointly.
This teamwork helps to:
- Reduce hospital stays
- Improve care for people with long-term conditions
- Make better use of resources
Many areas now have joint commissioning teams. These include staff from the NHS and council. They buy health and care services together.
Some places use 'alliance contracts'. These agreements help different organisations work as one team to provide care.
Regional Focus and Case Studies
Local authorities across England have adopted diverse procurement strategies to boost their regional economies. These approaches vary by region, with each area tailoring its methods to local needs and strengths.
Case Study: London's Approach
London's procurement strategy focuses on leveraging its vast economic power. The city's local authorities prioritise regional sourcing to support local businesses and stimulate growth.
Key elements of London's approach include:
- Supplier diversity programmes
- Social value considerations in contracts
- Emphasis on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
These initiatives have led to increased contract awards to London-based suppliers. The strategy has also fostered innovation and competition within the local business ecosystem.
Spotlight on East Midlands and North East
The East Midlands and North East regions have embraced collaborative procurement strategies. Local authorities in these areas often work together to achieve economies of scale and shared benefits.
In the North East, councils have formed buying consortiums to:
- Reduce costs
- Share best practices
- Increase bargaining power with suppliers
The East Midlands has seen success with joint initiatives addressing common challenges like social care resource allocation.
Success Stories from the South East
The South East region has made significant strides in sustainable procurement. Local authorities have integrated environmental and social considerations into their buying decisions.
Notable achievements include:
- Increased use of local food suppliers in school meal contracts
- Investment in renewable energy projects through procurement
- Support for apprenticeship schemes in construction contracts
These efforts align with the National Procurement Strategy for Local Government in England, which emphasises sustainability and social value. The South East's approach has resulted in tangible benefits for local communities and businesses.
Challenges and Mitigation
Local authorities face significant hurdles in procurement. These include the ongoing effects of Covid-19, supply chain disruptions, and staffing issues. Each challenge requires creative solutions and strategic planning to overcome.
Covid-19's Impact on Procurement
The pandemic drastically altered procurement practices for local authorities. Innovative solutions and elevated strategic planning became essential to address new challenges.
Many councils shifted to remote work, necessitating digital procurement processes. This change required new software and training for staff. Emergency purchasing became common, often bypassing standard procedures to obtain critical supplies quickly.
The crisis also highlighted the need for more resilient supply chains. Local authorities began prioritising local suppliers to reduce reliance on distant sources. This shift supported local economies while improving supply security.
Lessons learned from Covid-19 continue to shape procurement strategies. Councils now focus more on risk management and contingency planning in their purchasing decisions.
Facing the Challenges in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain disruptions pose ongoing issues for local authorities. Global events and market fluctuations can quickly impact the availability and cost of goods and services.
Key challenges include:
- Unpredictable lead times
- Price volatility
- Supplier insolvency risks
- Quality control issues
To mitigate these problems, councils are adopting new strategies:
- Diversifying supplier bases
- Implementing real-time tracking systems
- Building stronger relationships with key suppliers
- Increasing inventory of critical items
These approaches help create more robust and flexible supply chains. They allow local authorities to respond more effectively to disruptions and ensure continuity of services.
Recruitment and Retention in Procurement Teams
Staffing procurement departments presents a significant challenge for local authorities. The sector faces difficulties in attracting and keeping skilled professionals.
Reasons for this include:
- Competition from private sector jobs
- Limited career progression opportunities
- Budget constraints affecting salaries
- Lack of specialised training programmes
To address these issues, councils are taking several steps:
- Offering flexible working arrangements
- Developing clear career pathways
- Partnering with universities for graduate schemes
- Investing in professional development and training
By focusing on these areas, local authorities aim to build stronger, more stable procurement teams. This stability is crucial for maintaining effective purchasing practices and achieving long-term cost savings.
Monitoring and Reporting
Effective monitoring and reporting are crucial for local authorities to manage procurement spend and ensure value for money. These processes provide insights into expenditure patterns, supplier performance, and contract management effectiveness.
Understanding Procurement Expenditure
Local government procurement spending exceeds £70 billion annually. Tracking this expenditure is vital for budgeting and financial planning. Authorities must analyse spending across departments, categories, and suppliers.
Key areas to monitor include:
- Total spend by category
- Top suppliers by value
- Contract values and durations
- Payment terms and timelines
Regular spend analysis helps identify cost-saving opportunities and potential risks. It also supports strategic decision-making in procurement processes.
Authorities should use data visualisation tools to present spending information clearly. This aids in spotting trends and anomalies quickly.
The Use of Tussell for Spending Analysis
Tussell is a data intelligence platform that offers insights into public sector procurement. It provides local authorities with valuable information on contract awards and spending patterns.
Benefits of using Tussell include:
- Access to comprehensive contract award data
- Benchmarking against other authorities
- Identification of collaborative procurement opportunities
- Market intelligence on suppliers and competitors
Tussell's data helps authorities make informed decisions about suppliers and contracts. It also supports compliance with transparency requirements.
Authorities can use Tussell to monitor their own spending and compare it with others. This benchmarking can highlight areas for improvement in procurement practices.
Contract and Relationship Management
Effective contract management is essential for maximising value from procurement activities. It involves monitoring supplier performance, managing risks, and maintaining positive relationships.
Key aspects of contract management include:
- Regular performance reviews
- Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Managing contract variations and extensions
- Addressing disputes and issues promptly
Good relationship management helps authorities work collaboratively with suppliers. This can lead to innovation, cost savings, and improved service delivery.
Authorities should implement robust systems for tracking contracts and supplier interactions. Regular reporting on contract performance helps identify areas for improvement and inform future procurement decisions.
Education and Workforce Development
Local authorities are investing in education and training to build skilled procurement teams. These efforts aim to improve strategic purchasing and commercial behaviours.
Apprenticeships Within Procurement Teams
Apprenticeships offer a practical way for local authorities to develop procurement talent. Many councils now partner with training providers to offer procurement-specific apprenticeships.
These programmes combine on-the-job learning with classroom training. Apprentices gain hands-on experience in areas like contract management and supplier negotiations.
The Local Government Association encourages councils to use apprenticeships to build capability. This helps create a pipeline of skilled professionals familiar with public sector procurement.
Educational Programmes for Strategic Procurement
Universities and professional bodies now offer specialised courses in public procurement. These programmes teach strategic skills like category management and social value creation.
Short courses and workshops help existing staff update their knowledge. Topics often include new regulations, digital procurement tools, and sustainable purchasing.
Some local authorities partner with business schools to develop custom training. This ensures learning aligns with specific council priorities and challenges.
Workforce Development and Training
Ongoing training is crucial for procurement teams to stay current. Many councils now have structured development plans for procurement staff.
These plans may include:
- Mentoring programmes
- Job rotations to gain diverse experience
- Attendance at industry conferences
- Online learning platforms for flexible skill development
Training often focuses on behaving commercially and delivering value for money. This helps staff balance commercial skills with public sector ethics.
Councils are also investing in leadership development for senior procurement roles. This supports succession planning and helps retain top talent.
Conclusion
Regional procurement by local authorities is changing rapidly. New trends focus on supporting local economies and small businesses. This helps create jobs and boost growth in communities.
Technology plays a big role in modernising procurement processes. Online platforms make bidding easier for small firms. Data analytics help councils make smarter purchasing decisions.
Sustainability is now a key factor in procurement choices. Councils want suppliers with green practices. This pushes businesses to be more eco-friendly.
Collaboration between councils is growing. Shared procurement can lead to cost savings. It also gives smaller councils more buying power.
Skills gaps remain an issue for some authorities. Training staff in modern procurement methods is crucial. This ensures they can handle complex contracts effectively.
The future of regional procurement looks promising. With the right approaches, it can transform public services and boost local economies. Ongoing learning and adapting to new trends will be vital for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Local authorities face complex challenges in procurement. Key issues include national policies, legal requirements, and effective strategies for public purchasing. Regional trends shape how councils approach these areas.
What are the key components of the National Procurement Policy Statement impacting local councils?
The National Procurement Policy Statement guides local council purchasing. It focuses on social value, commercial delivery, and skills.
Councils must consider how procurement can improve local economic, social and environmental wellbeing. The statement emphasises strategic supplier management and developing procurement expertise.
How do Local Government Procurement Guidelines influence the purchasing strategies of local authorities?
Local Government Procurement Guidelines set standards for council buying practices. They promote transparency, fairness and value for money.
The guidelines encourage competitive tendering and clear evaluation criteria. They also stress the importance of contract management and supplier relationships.
What are the implications of the Procurement Act 2023 for regional procurement practices?
The Procurement Act 2023 aims to simplify and modernise public purchasing. It introduces more flexibility in procurement procedures for local authorities.
The Act shifts focus from 'most economically advantageous tender' to 'most advantageous tender'. This allows councils to consider broader value beyond just price.
What steps are involved in the government tender process within local councils?
The tender process typically begins with identifying a need and planning the procurement. Councils then publish a tender notice and provide detailed specifications.
Suppliers submit bids, which are evaluated against set criteria. The council selects the winning bid and awards the contract. Contract management follows to ensure delivery.
How do local authorities ensure compliance with national procurement strategies?
Councils use internal policies and procedures aligned with national strategies. They often have dedicated procurement teams to oversee compliance.
Regular training keeps staff updated on procurement rules. Internal audits and external reviews help ensure adherence to national strategies.
Can you outline the three primary strategies used in public procurement by local governments?
The first strategy is open tendering, which invites all qualified suppliers to bid. This promotes competition and transparency.
The second is restricted tendering, where only pre-qualified suppliers can bid. This is useful for complex or specialised purchases.
The third is framework agreements, which establish terms for future contracts. These save time and resources for recurring purchases.